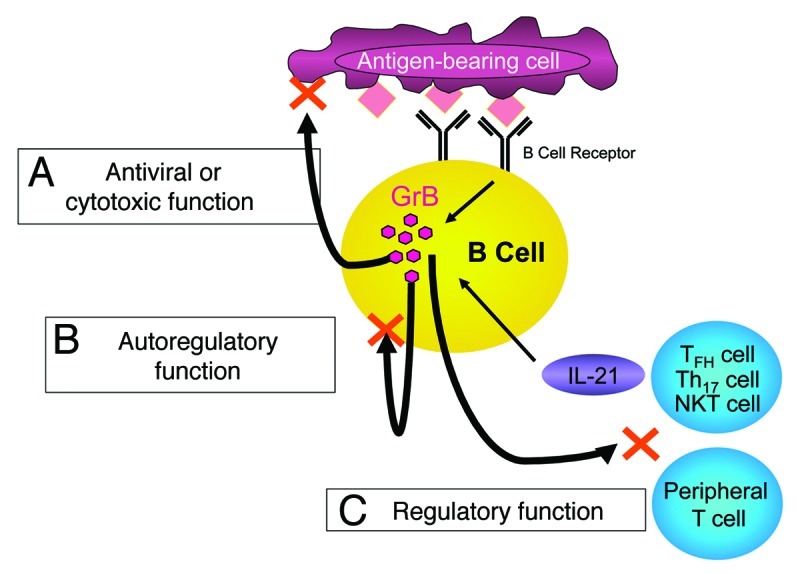
Figure 1. Possible immunological functions of granzyme B-secreting B cells. B cell-derived granzyme B (GrB) in the context of interleukin-21 (IL-21) stimulation and B-cell receptor (BCR)-engagement may mediate the following functions. (A) The direct, specific and MHC-independent recognition of antigens may stimulate cytotoxic or B cells with antiviral properties, particularly during the early phases of infections. (B) The leakage of GrB in the cytoplasm may result in the apoptotic demise of autoreactive B cells. (C) B cells may acquire a regulatory phenotype, involving GrB expression, that results in suppressive effects on other immune cells.
