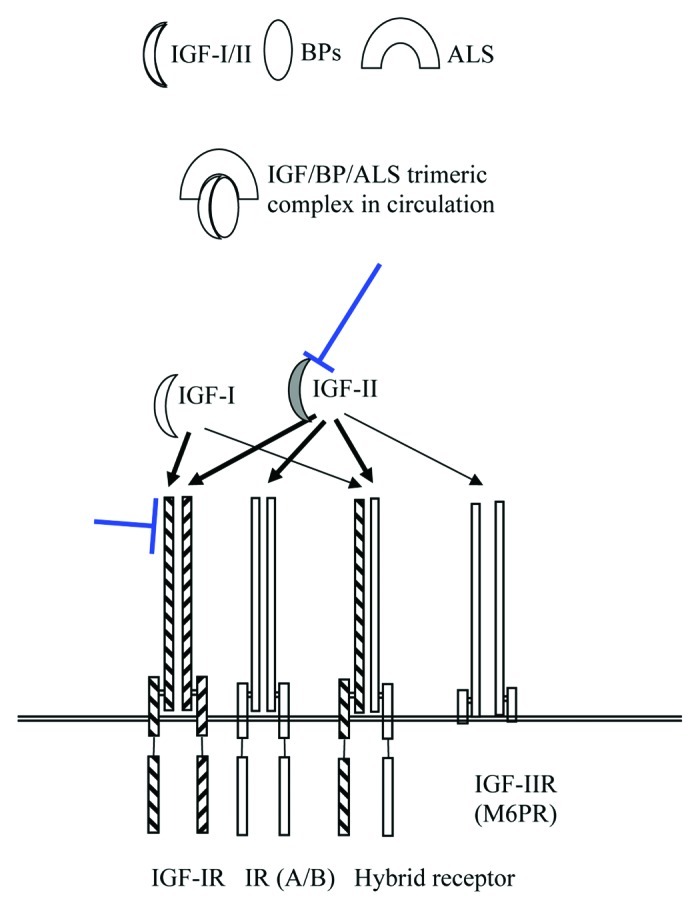
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the main components of the IGF system. While both IGF-I and IGF-II bind to IGF-1R at high affinity, only IGF-II binds to the hybrid receptor at high affinity. IGF-II also binds to the insulin receptor and to IGF-2R (also known as mannose-6-phosphate receptor), which lack the cytoplasmic activation domain and functions as the regulator of circulating IGF-II levels. Because of a feedback mechanism, elevation of IGF-I levels has been observed following IGF-1R antibody therapy. IGF-II is produced by many childhood tumors such as neuroblastoma, Ewing’s sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, and osteosarcoma. Thick arrows represent high affinity binding of IGFs to the receptors. Antibodies targeting IGF-1R and IGF-II (flat arrows) may block signaling from both ligands.
