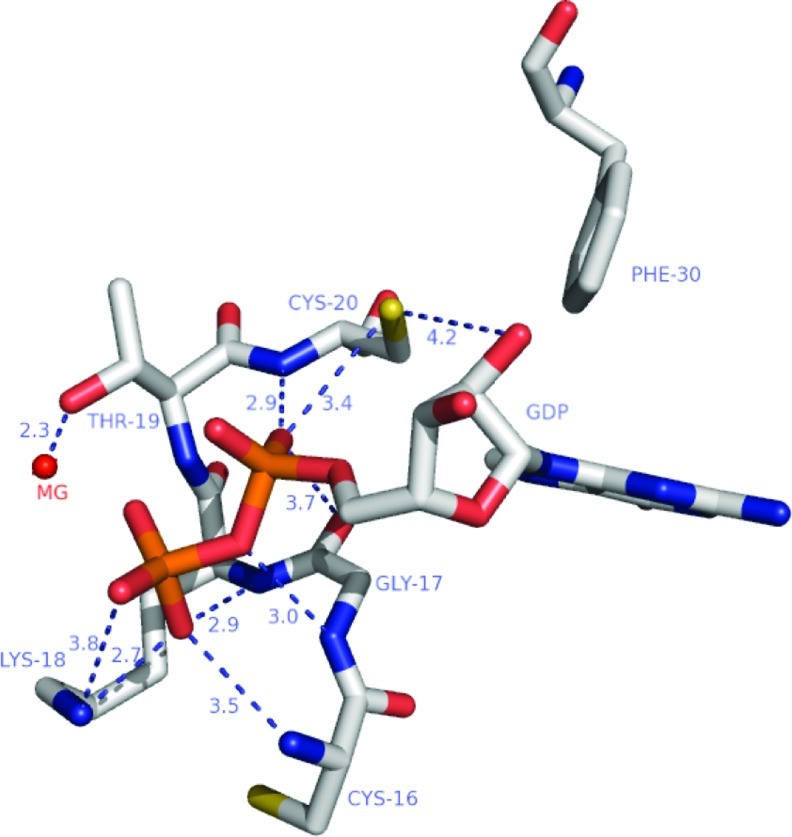
FIG. 3.
The phosphoryl-binding loop of RhoA bound to GDP. The phosphoryl-binding loop of Rho GTPases, including Cys20 and Cys16, makes several critical hydrogen bonds with the bound nucleotide. Oxidation of RhoA by 1e− mediated oxidants results in nucleotide hydrolysis and dissociation similar to Ras GTPases; however, oxidation of RhoAC20 by 2e− oxidants likely results in perturbation of nucleotide binding and an increase in nucleotide exchange. According to data using phenyl-arsine oxide and peroxide (22), a mixed disulfide or disulfide can form between RhoA Cys20 and Cys16 upon oxidation of Cys20. When the disulfide bond is formed, it occludes nucleotide binding and inactivates the GTPase. However, nucleotide binding can be restored upon reduction of the disulfide, and this cycling results in guanine nucleotide exchange (GDP for GTP) and activation of the GTPase. Figure adapted from PDB ID:1FTM using Pymol. The hydrogen bonds are shown as blue dotted lines with the distances in angstroms. Color scheme: carbon, white; sulfur, yellow; nitrogen, blue; oxygen, salmon; phosphate, orange; and magnesium, red. (To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars).