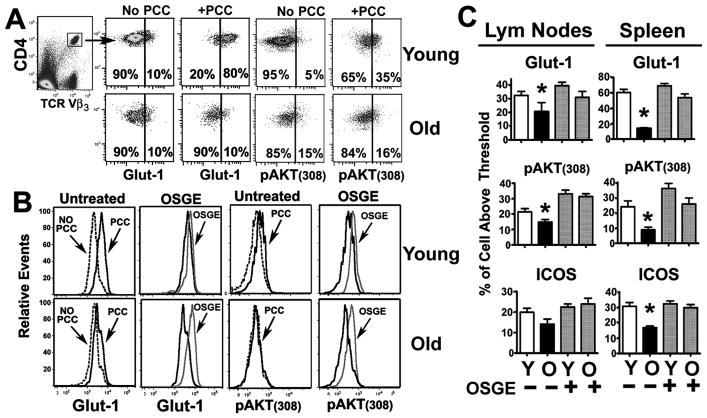
Figure 2. Age impairs, and OSGE improves, induction of Glut-1, pAKT, and ICOS in adoptively transferred CD4 T cells.
A) pAKT(308) levels and Glut-1 expression in resting and activated CD4 T cells. CD4 cells from AND mice were adoptively transferred to non-primed (no PCC) or PCC-primed CD4KO mice, and spleens and lymph nodes were collected 16 hours later. T cells were purified and stained for CD4/VB3-TRC, Glut-1, and pAKT(308). Gated CD4+VB3+ cells were used to evaluate the expression of Glut-1 or pAKT(308) in resting or activated CD4 T cells. The vertical line shows the threshold used to distinguish Glut-1 and pAKT(308)low from Glut-1 and pAKT(308)hi cells for the calculations illustrated in panel (C). B) Effect of aging and OSGE treatments on Glut-1 expression and pAKT(308). Representative analysis of the effects of aging and OSGE on Glut-1 expression and pAKT(308) in CD4 T cells. Untreated or OSGE-treated CD4 T cells from young (top histograms) or old (bottom histograms) AND mice were adoptively transferred to CD4KO hosts primed with PCC (dark lines) or left unprimed (dot lines). Glut-1 expression was analyzed as described in panel A above. Priming with PCC increased Glut-1 expression and pAKT on gated CD4VB3+ cells from young, but not from old, donor mice. Pre-treatment with OSGE (light lines) enhanced Glut-1 and pAKT in primed CD4 T cells from old donors. C) Quantification of the effects of aging and OSGE on Glut-1, pAKT, and ICOS. Each bar represents mean percentage (± SEM) of CD4 T cells from 8 young and 4 old AND donor mice with enhanced expression of Glut-1 or ICOS and increased AKT phosphorylation. The asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance with respect to untreated young cells in primed hosts.