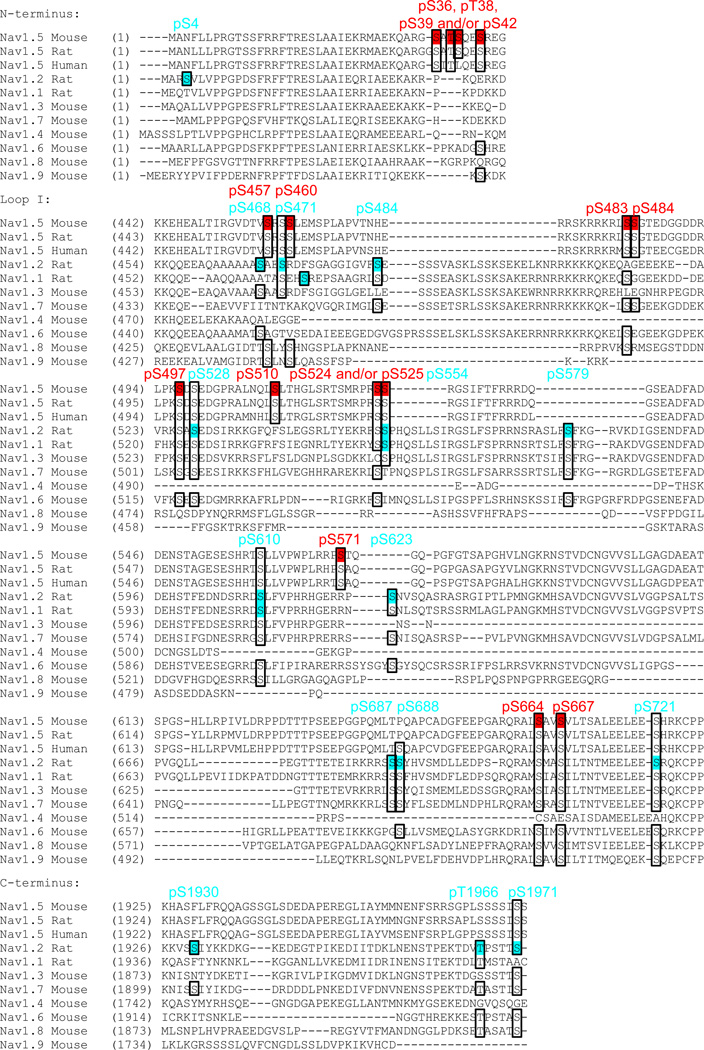
Figure 6.
Sequence alignment and conservation of phosphorylation sites across Nav channel homologues and species. The multiple amino acid sequence alignment was constructed using the ClustalW algorithm (from the Vector NTI 9.1.0 software, Invitrogen), and the following NCBI Reference Sequences were used: NP_067519.2 for mouse Nav1.5, NP_037257.1 for rat Nav1.5, NP_932173.1 for human Nav1.5, NP_036779.1 for rat Nav1.2, NP_110502.1 for rat Nav1.1, NP_061202.3 for mouse Nav1.3, NP_061340.2 for mouse Nav1.7, NP_573462.2 for mouse Nav1.4, NP_001070967.1 for mouse Nav1.6, NP_001192250.1 for mouse Nav1.8, and NP_036017.3 for mouse Nav1.9. Alignment results of portions of the N-terminus, loop I (interdomain I-II) and the C-terminus are shown only. The native mouse cardiac Nav1.5 phosphorylation sites identified in the present study are highlighted in red, and compared directly with the native phosphorylation sites identified on the rat brain Nav1.2 (and Nav1.1) proteins13 (in blue). The conservation of serines and threonines identified as in situ phosphorylation sites in the two studies is presented in boxes.