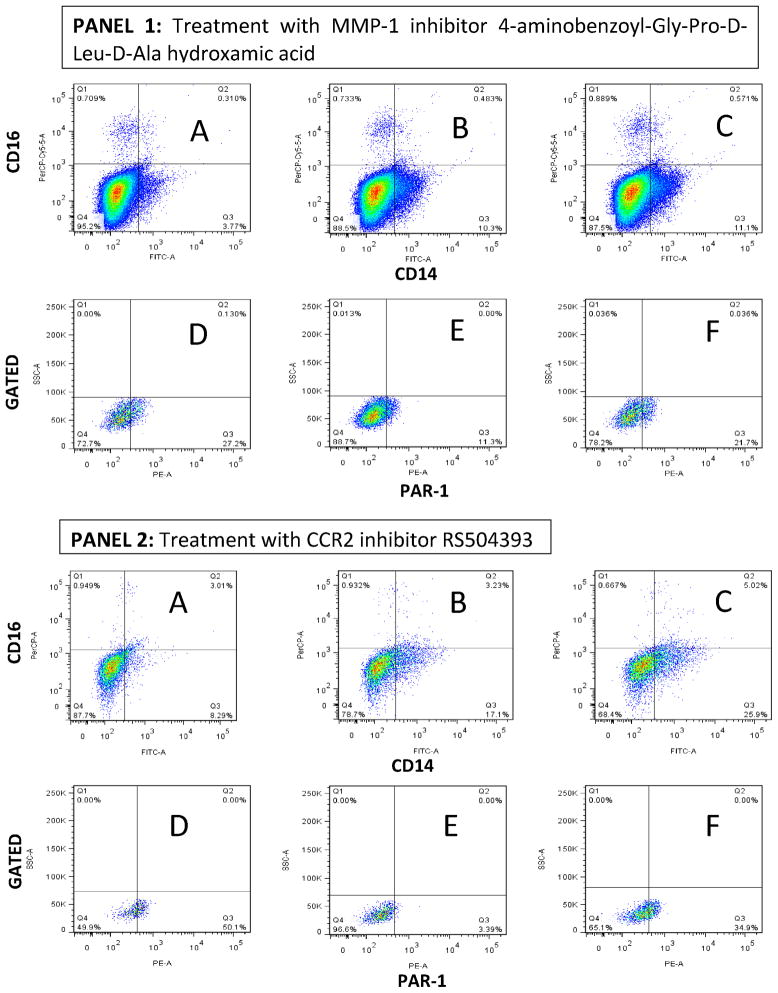
Figure 5. Down-regulation of PAR-1 expression by exposure of THP-1 cells to sonicated H37Rv M. tuberculosis and counter effect of MMP-1 and CCR-2 inhibitor.
We used three-color FACS analysis for these experiments. Exposure of quiescent THP-1 cells to sonicated H37Rv M. tuberculosis for 24 hr induced the differentiation of these cells into CD14-positive/CD16-negative cells. In Panels 1 and 2, Section A shows a low proportion of CD14-positive/CD16-negative cells in quiescent THP-1 cells; Section B shows an increment in the proportion of CD14-positive/CD16-negative THP-1 cells in response to sonicated H37RV M. tuberculosis exposure.; Section C shows minimal (non-significant) variation in this response to sonicated H37Rv M. tuberculosis exposure in the presence of the MMP-1 inhibitor (Panel 1) or CCR2 inhibitor (Panel 2). In Sections D, E, and F of Panel 1, we show that the presence of MMP-1 inhibitor 4-Aminobenzoyl-Gly-Pro-D-Leu-D-Ala hydroxamic peptide prevents the down-regulation of PAR-1 expression by THP-1 cells exposed to sonicated H37Rv M. tuberculosis exposure. In Sections D, E, and F of Panel 2, we show that the presence of CCR2 inhibitor RS504393 also prevents the down-regulation of PAR-1 expression by THP-1 cells exposed to sonicated H37Rv M. tuberculosis exposure. We acquired 100,000 events for experiments in Panel 1, while we acquired 10,000 events for experiments in Panel 2, according to the number of live cells gathered in each experiment. Of note, the MMP-1 inhibitor was dissolved in incomplete RPMI while the CCR2 inhibitor was dissolved in DMSO to obtain a DMSO final culture concentration of 0.01%. Three experiments were done for the assessment of each inhibitor.