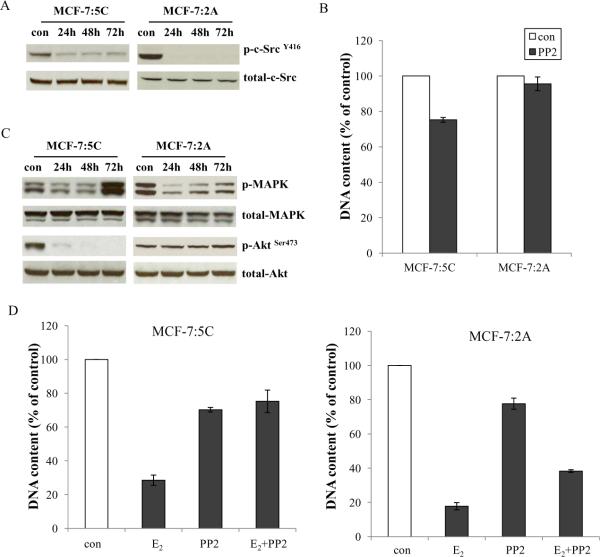
Figure 3. Effects of the c-Src inhibitor on ER positive endocrine resistant cell lines.
3A. Blocking c-Src phosphorylation in endocrine resistant ER positive cells. MCF-7:5C and MCF-7:2A cells were treated with PP2 (5μM) at time points as indicated and cell lysates were harvested. Phosphorylated c-Src was detected by immunoblotting with primary antibody. Immunoblotting for total c-Src was used for loading control. 3B. Growth inhibitory effects of PP2 on endocrine resistant ER positive cells. MCF-7:5C and MCF-7:2A cells were seeded in 24-well plates in triplicate. After one day, the cells were treated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO) and PP2 (5μM) respectively in culture medium. The cells were harvested after 7 days treatment and total DNA was determined as above. 3C. Signaling pathways changes in endocrine resistant ER positive cells after PP2 treatment. Cell lysates were harvested as above. Phosphorylated MAPK and Akt were examined by immunoblotting with primary antibodies. Immunoblotting for total MAPK and Akt were used for loading controls. 3D. The PP2 blocked E2-induced inhibition in MCF-7:5C and MCF-7:2A cells. MCF-7:5C cells were seeded in 24-well plates as above. After one day, the cells were treated with vehicle (0.1% EtOH), E2 (10−9mol/L), PP2 (5μM), and E2 (10−9mol/L) plus PP2 (5μM) respectively. The cells were harvested after 7 days treatment and total DNA was determined as above. MCF-7:2A cells were seeded in 6-well plates. After one day, the cells were similarly treated as in MCF-7:5C cells. The cells were harvested after 14 days treatment and total DNA was determined as above.