Fig. 5.
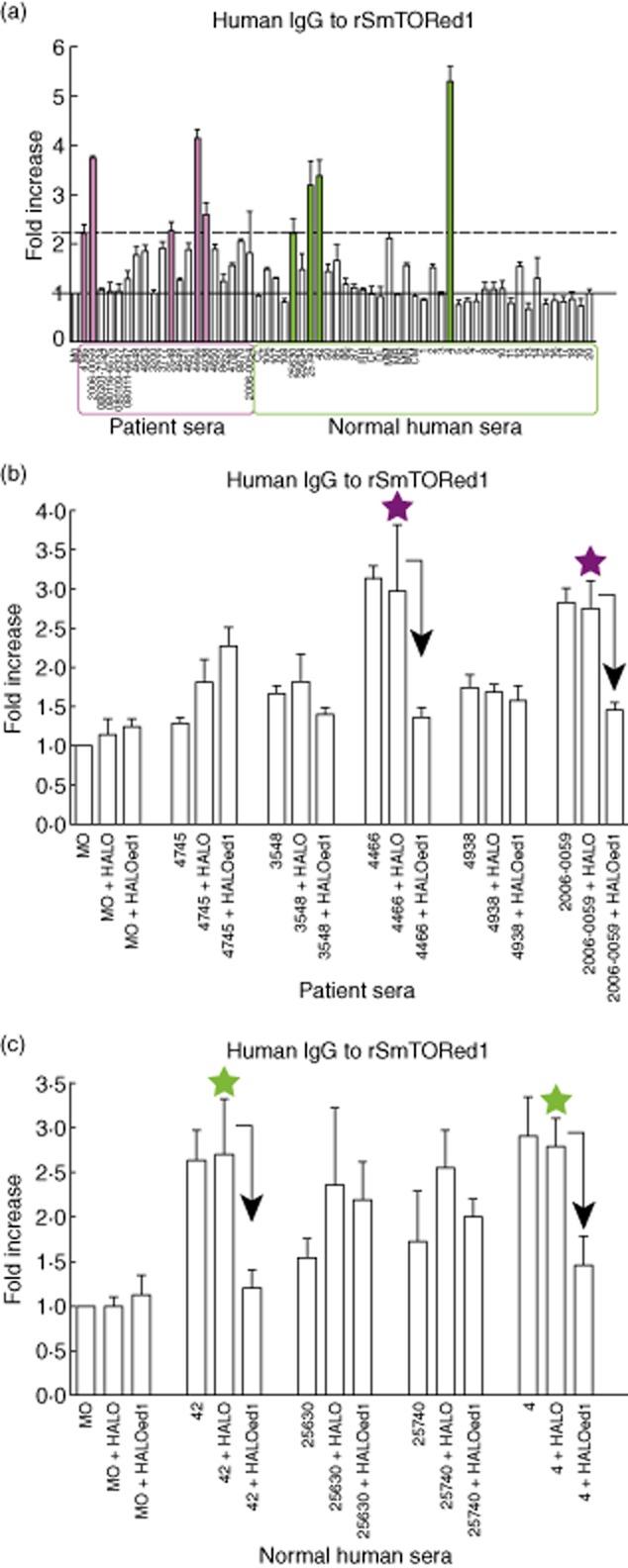
Detection of human immunoglobulin (Ig)G to recombinant first extracellular domain of Schistosoma mansoni tetraspanning orphan receptor (SmTORed1) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and confirmation of specificity by competition ELISA using Halo-tagged bead-bound fusion constructs. (a) Total IgG levels in patients (archived anonymized sera, purple box) and normal human sera (NHS) (green box) normalized to control serum monocytes (MO, grey bar). The black solid line set at 1 corresponds to the mean of absorbance measuring control MO [mean optical density (OD) ± standard deviation (s.d.) (n = 9): OD450 nm = 0·176 ± 0·05], that was set to 1 in order to picture patient and NHS values normalized to one control serum value. The dashed black line was set at an arbitrary threshold and marks the lower limit of a fold-increase value considered as a positive signal. Five (filled purple bars) out of 20 patients and four (filled green bars) out of 40 patients were tested as positive. The results of three different experiments performed in duplicate are shown. Error bars indicate s.d. of the means. (b,c) Measurement of IgG specificity in schistosomiasis patients (b) and NHS (c). OD450 values measured were normalized to mean values recorded for the control sample (MO, OD450 nm = 0·243 ± 0·06, n = 7) and indicated as fold increased values. Prior to IgG measurement, individual sera were preincubated with Halo constructs coupled to magnetic beads: no competition (sample + no beads), with HaloTag alone (sample + Halo) or Halo-SmTORed1 (Haloed1). Stars indicate specific IgG to rSmTORed1 in the corresponding serum, tested by competition ELISA. Bars represent the mean values of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate s.d. of the means. Arrows indicate a significant decrease (>40%) in signal due to depletion of specific antibodies by preincubation with Haloed1.
