Fig. 4.
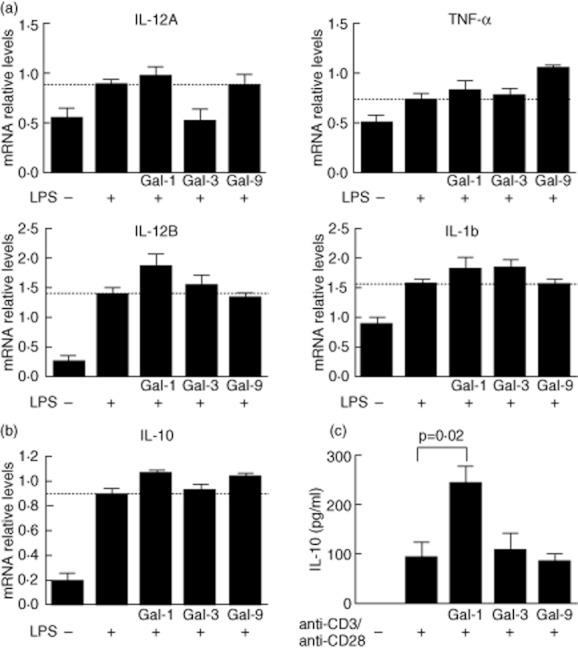
Galectin (gal)-1 and gal-9 induce interleukin (IL)-10 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells of healthy donors. (a) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) (5 × 105) were incubated on p24 plates in the presence or not of 100 ng/ul lipopolysaccharide (LPS) plus 10 μg/ml gal-1, gal-3 or gal-9. After 24 h of culture, IL-12A, IL-12B, tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α and IL-1b expression were analysed by reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT–PCR). Bars correspond to mean ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.) from five independent experiments. Dashed lines indicate LPS-induced cytokine expression. Differences among groups were tested by one-way analysis of variance (anova) test. mRNA levels are expressed as arbitrary units respect to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) expression (b). mRNA IL-10 expression of PBMC treated as in (a), bars correspond to mean ± s.e.m. from five independent experiments. Dashed line indicates LPS-induced IL-10 expression. (c) IL-10 secretion by peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-C28 in the presence or absence of gal-1, gal-3 or gal-9. PBLs (2 × 106/ml) were incubated on p24 plates precoated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28, where indicated 10 μg/ml of gal-1, gal-3 or gal-9 were added. IL-10 production was tested using bead-based immunoassay by flow cytometry. Bars correspond to mean ± s.e.m. from four independent experiments. Differences among groups were tested by one-way anova test.
