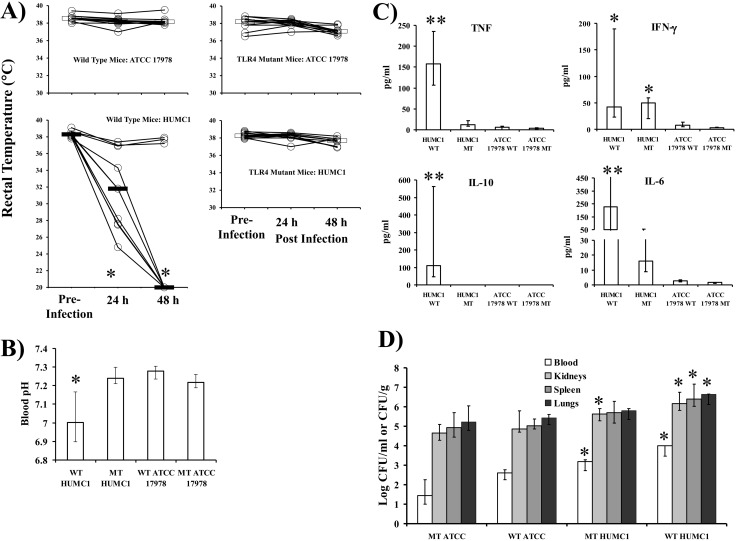
FIG 2 .
Lethally infected wild-type mice had septic shock, whereas TLR4-mutant mice did not. (A) Rectal temperatures taken from mice infected with A. baumannii HUMC1 or ATCC 17978 (the same mice in Fig. 1; n = 10 mice per group, except for 9 in the wild-type HUMC1-infected group). Temperatures were taken at the same time (8 to 9 AM) daily before and for 2 days after infection (wild-type mice began dying on day 2). *, P < 0.05 versus preinfection findings. (B) Blood pH at 48 h of infection was measured by using i-STAT cartridges from separate C3H/FeJ or C3H/HeJ (TLR4-mutant) mice infected with 2 × 107 A. baumannii HUMC1 or ATCC 17978 bacteria (n = 16 mice per group from 2 experiments, except for 8 mice for HUMC1-infected wild-type mice). *, P < 0.05 versus results for other groups. (C) Serum inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels were measured at 48 h of infection in C3H/FeJ or C3H/HeJ (TLR4-mutant) mice. n = 8 mice per group. **, P < 0.05 versus results for all other groups; *, P < 0.05 versus results for ATCC 17978 groups. (D) Blood and tissue bacterial burden at 48 h of infection differed between mice infected with 2 × 107 HUMC1 and ATCC 17978 bacteria (n = 12 mice per group from 2 experiments) but not between mutant and wild-type mice. *, P < 0.05 versus results for mice infected with ATCC 17978. Median and interquartile ranges are graphed.