FIG 5 .
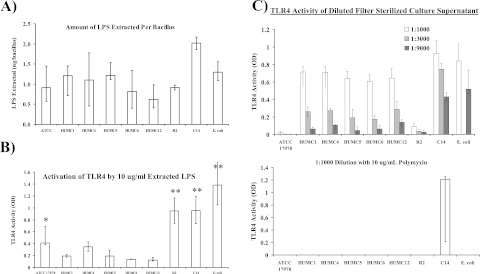
In vitro correlate of in vivo virulence. (A) LPS content (ng/bacillus) was similar across strains of highly varying virulences (e.g., HUMC1 versus ATCC 17978 versus R2). Results are from at least two separate extractions, each done in duplicate. (B) TLR4-activating potency of extracted LPS was higher for R2 and C14 than all other A. baumannii strains (**, P < 0.05 versus results for all other strains except E. coli). Of the colistin-susceptible A. baumannii strains, TLR4-activating potency was highest among A. baumannii ATCC 17978, which was avirulent (*, P < 0.05 versus HUMC strains). Results are from a minimum of two assays per strain, each done in duplicate. (C) Filter-sterilized culture supernatant induced a much stronger TLR4 signal from strains that caused lethal infections in vivo than from avirulent strains. Also, addition of polymyxin blocked the TLR4 activation from all strains except those highly resistant to colistin (C8 and C14), which were not affected by polymyxin. Results are from a minimum of three assays per strain, each done in duplicate. For all panels, median and interquartile ranges are graphed.