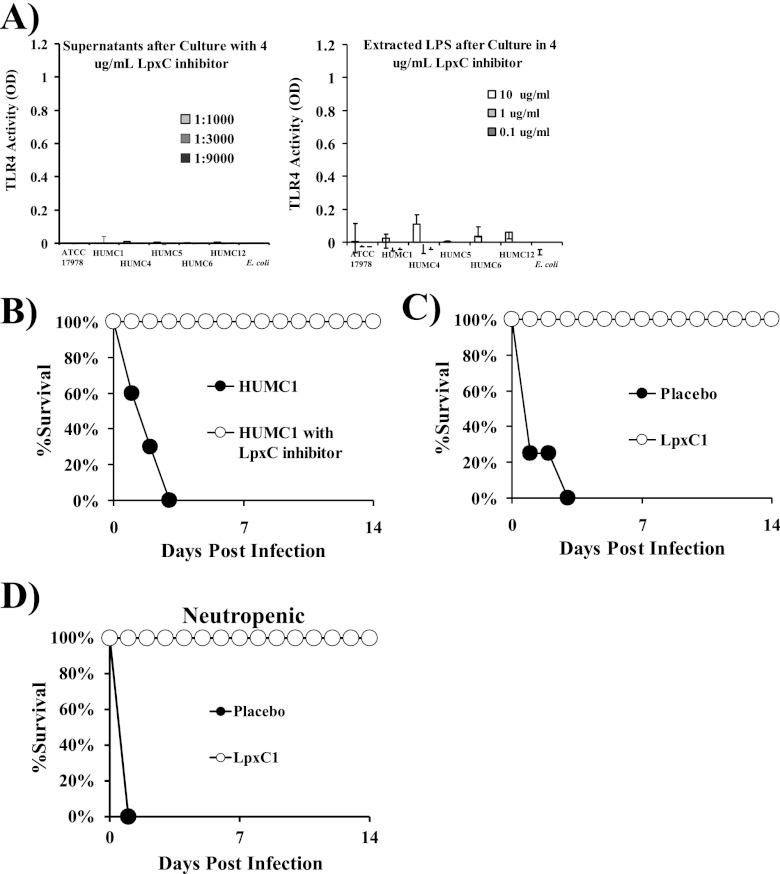
FIG 6 .
Inhibition of LPS biosynthesis with an inhibitor of LpxC blocked TLR4 activation in vitro and abrogated virulence in vivo. (A) TLR4-activating potency of filtered culture supernatant and extracted LPS from A. baumannii strains passaged to log phase in the presence of 4 µg/ml of LpxC inhibitor (LpxC-1). The results with LpxC-1 were run concurrently with those without LpxC-1 (compare signal with and without LpxC-1 inhibitor in Fig. 5C versus Fig. 6A). (B) Survival of wild-type C3H/FeJ mice (n = 10 per group) which were either infected with normal A. baumannii HUMC1 and treated with a placebo (40% cyclodextrin in water i.v. once daily) for 3 days starting on the day of infection or infected with A. baumannii HUMC1 that was cultured overnight and during log passage in the presence of 4 µg/ml of LpxC inhibitor and treated with LpxC-1 (100 mg/kg in 40% cyclodextrin i.v.) for 3 days postinfection. (C) Survival of wild-type C3H/FeJ mice (n = 10 per group) which were infected with A. baumannii HUMC1 and treated with a placebo (40% cyclodextrin in water) or LpxC-1 (100 mg/kg in 40% cyclodextrin i.v.) starting 1 h after infection and for 3 days postinfection. (D) Survival of BALB/c mice (n = 11 in the placebo group; n = 10 in the LpxC1-treated group) made neutropenic with cyclophosphamide, infected with A. baumannii HUMC1, and treated with placebo or LpxC-1 starting after infection and for 3 days postinfection.