Abstract
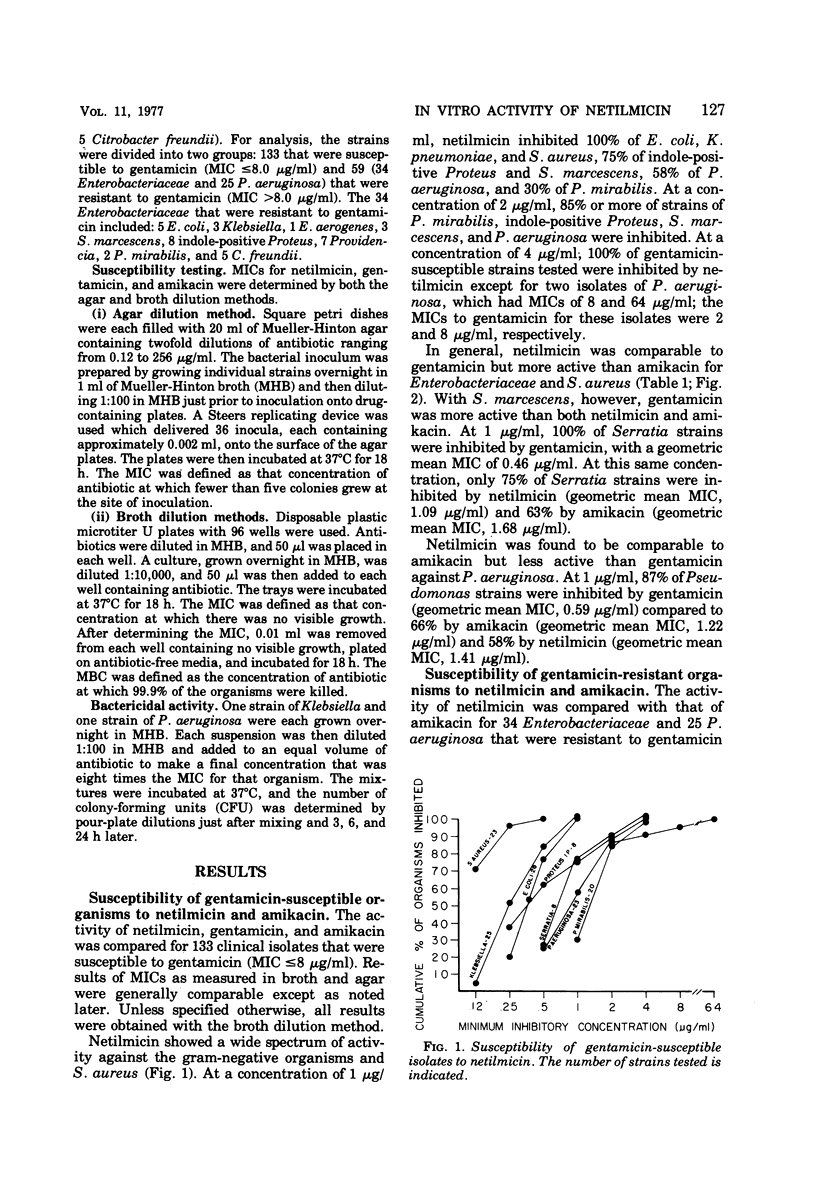
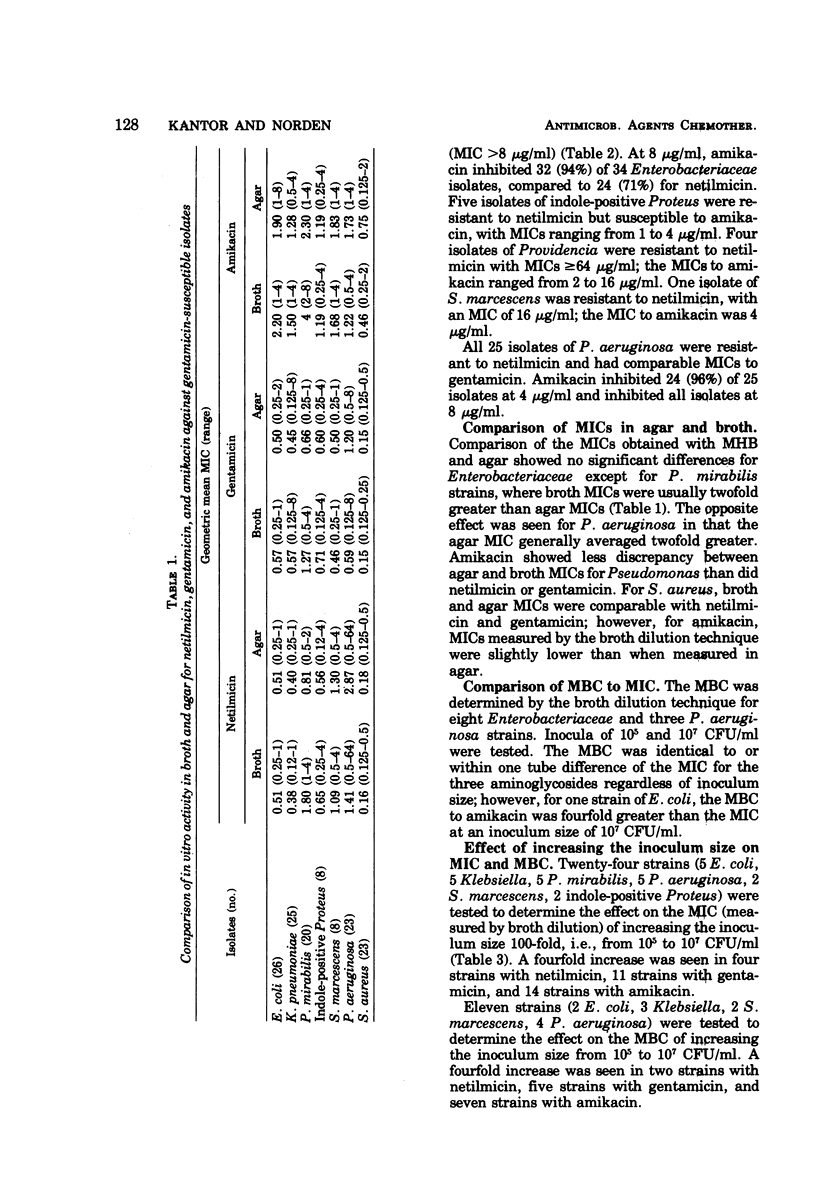
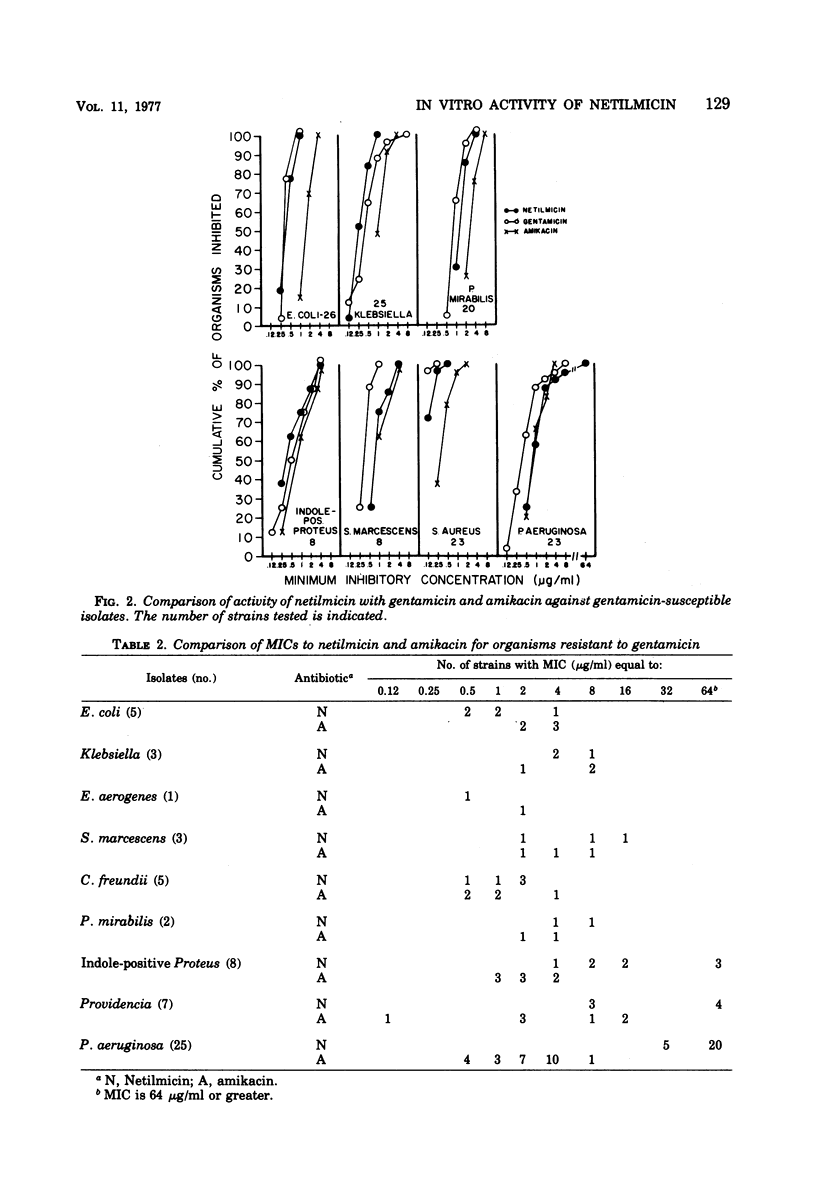
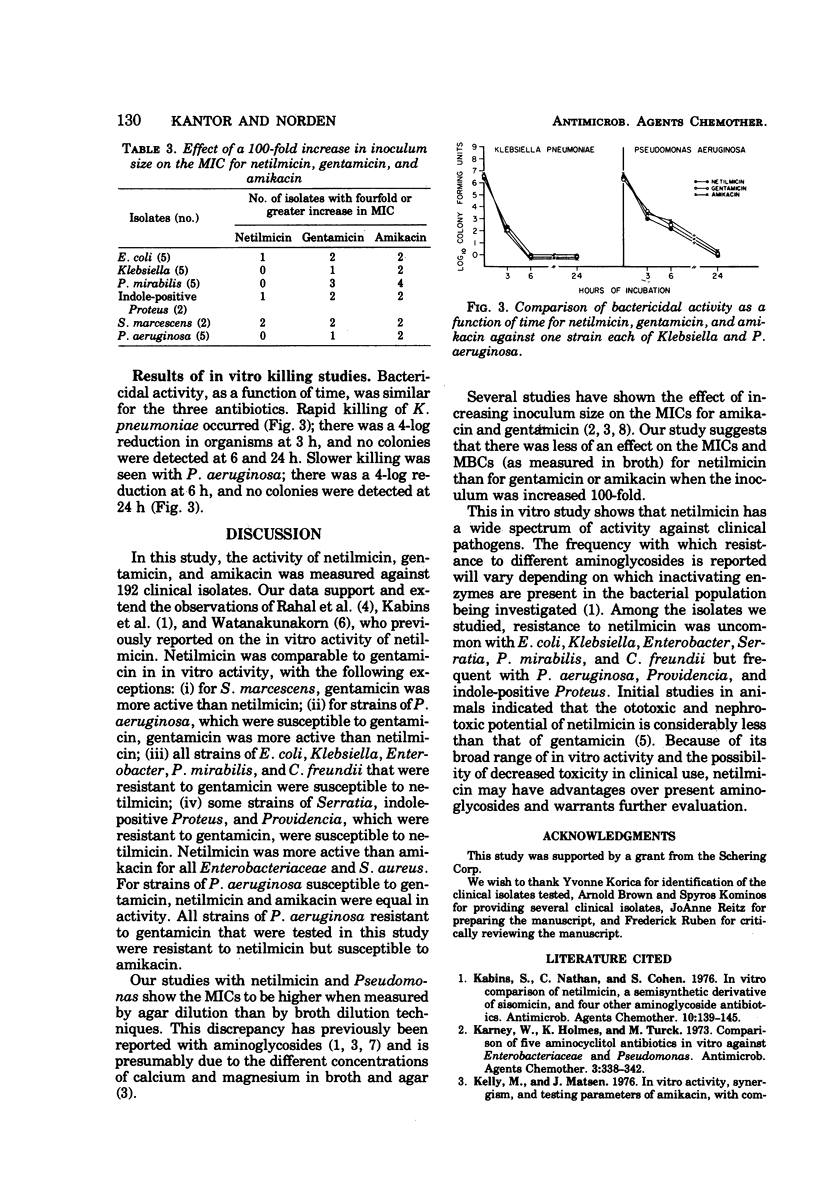
The in vitro activity of netilmicin (Sch 20569), a new semisynthetic derivative of gentamicin, was compared with that of gentamicin and amikacin. One hundred and ninety-two clinical isolates of Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus were tested using both agar and broth dilution techniques. Netilmicin was comparable to gentamicin, with the following exceptions: (i) for Serratia marcescens and P. aeruginosa, gentamicin was more active than netilmicin; (ii) all strains of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Proteus mirabilis, and Citrobacter freundii, which were resistant to gentamicin, were susceptible to netilmicin; (iii) some strains of S. marcescens, indole-positive Proteus, and Providencia, which were resistant to gentamicin, were susceptible to netilmicin. Netilmicin was more active than amikacin for all Enterobacteriaceae and S. aureus and equal to amikacin in activity against gentamicin-susceptible strains of P. aeruginosa. All strains of P. aeruginosa, resistant to gentamicin, were also resistant to netilmicin but were susceptible to amikacin. Minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) obtained with broth and agar showed no significant differences except for P. mirabilis, where broth MICs were twofold greater than agar MICs, and for P. aeruginosa, where agar MICs were twofold higher than broth MICs. The minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) was either identical to or within one twofold dilution of the MIC for the strains tested. A 100-fold increase in inoculum size produced less increase in MIC and MBC with netilmicin than with gentamicin or amikacin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kabins S. A., Nathan C., Cohen S. In vitro comparison of netilmicin, a semisynthetic derivative of sisomicin, and four other aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):139–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karney W., Holmes K. K., Turck M. Comparison of five aminocyclitol antibiotics in vitro against Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Mar;3(3):338–342. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.3.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr, Simberkoff M. S., Kagan K., Moldover N. H. Bactericidal efficacy of Sch 20569 and amikacin against gentamicin-sensitive and -resistant organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):595–599. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C. Comparative in vitro activity of Sch 20656, netilmicin, gentamicin, and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Aug;10(2):382–383. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Activity of five aminoglycoside antibiotics in vitro against gram-negative bacilli and Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):617–625. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu P. K., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparative in vitro activity of three aminoglycosidic antibiotics: BB-K8, kanamycin, and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Aug;4(2):133–139. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


