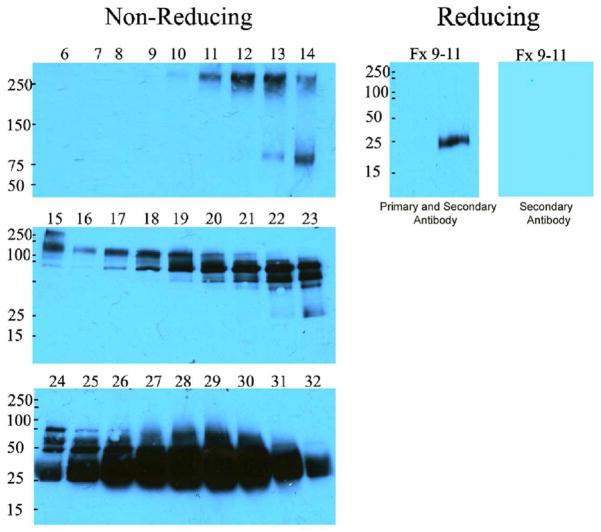
Figure 1.
Urine was fractionated by cation exchange chromatography and fractions containing immunoreactive NGAL species were then separated by filtration chromatography (Left Panels). Note that the monomer (23–26KDa, fractions 24–32) comprised the majority of immunoreactive NGAL, but additional species can be found at 75KD (fractions 19–23), 125KDa (fractions 15–18) and >250KDa (fractions 9–11). When the latter were pooled and reduced, the only immunoreactive species was the monomer (Right). These data show that in advanced CKD, a proportion of NGAL is associated with other proteins.