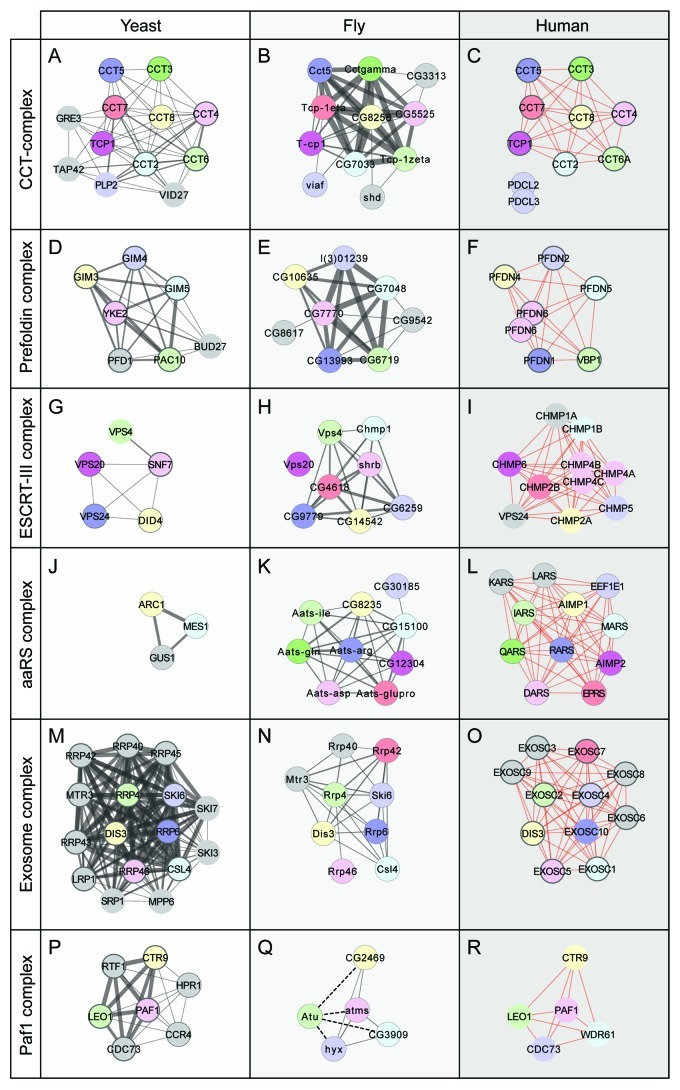
Figure 2. Patterns of Protein complex evolution. Comparison of protein complexes defined in DPiM (center panels, fly) with the same functional complexes from yeast (left panels, using MIPS, CYC2008) and human cells (right panels, using REACTOME, CORUM). Protein partners found in one database have thinner outlines while proteins found in both databases have thicker outlines. Proteins with obvious sequence similarity are colored identically and arranged in similar location for all three species. In case of multiple paralogs, the protein with highest sequence homology is considered as the corresponding homolog. Proteins shown as gray circles are members that have no clear sequence similarity with others, although they may have similar names. The thickness of gray lines connecting the proteins is proportional to the score/weight of the interaction, while red lines connecting human proteins are unweighted interactions in the databases. (A–C) The CCT (chaperonin-containing T-complex) comprises nine conserved proteins conserved in all three species, while in yeast and fly, a small number of other proteins are also found to be associated. (D–F) The Prefoldin complex does not show significant variation from yeast to human, with only minor addition or subtraction of new complex members (two Ensembl gene IDs for PFDN6). (G–I) The ESCRTIII complex is a multiprotein assembly with a conserved role in endocytosis. In yeast, it contains five members, which are retained in both fly and human; although the VPS24 components of yeast and human do not share noticeable sequence similarity. In DPiM, the complex has also been found to be associated with the Flotillin complex (not shown) in fly cells. (J–L) The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases consist of both conserved and variant subunits, due to their derivation by both paralogous evolution and horizontal gene transfer. Comparison shows that fly and human complexes are very similar, while in yeast, only a subset of these is found. (M–O) The Exosome (RNase) complex in all three species has six conserved core members. The other proteins, despite similar names, do not appear to be closely related in sequence, exemplifying how the same functional complex can have different protein components across species. (P–R) The Paf1 complex is involved in RNA Polymerase II function, and one member, Atu has sub-threshold interaction scores (dotted lines, Q) with other subunits in DPiM.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.