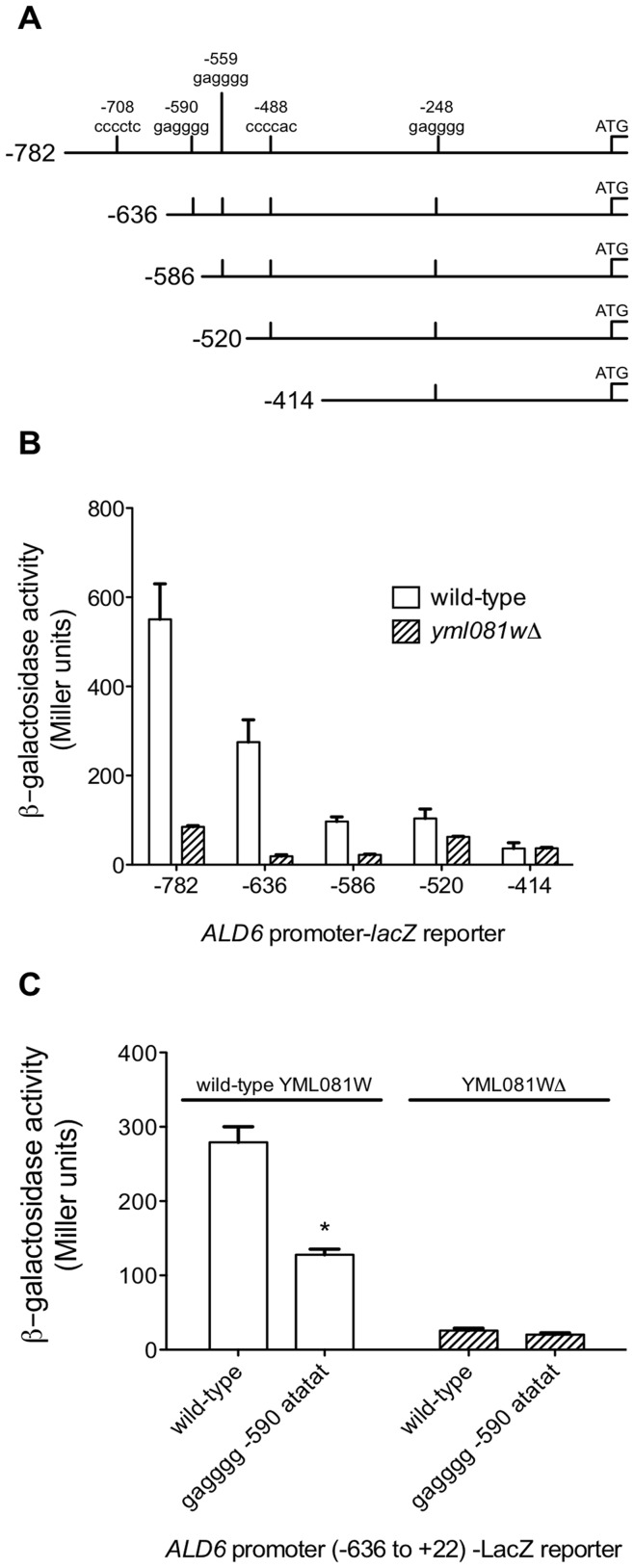
Figure 5. Yml081Wp regulates the ALD6 promoter.
(A) A schematic diagram of the ALD6 promoter sequence. Numbers on the left indicate the position of the first nucleotide in the promoter construct relative to the start codon. The positions and sequences of sites matching the previously published Yml081Wp binding sites are highlighted above the full-length promoter. (B) LacZ reporter activity from the ALD6 promoter. Reporter plasmids carrying ALD6 promoter fragments of the indicated lengths were transformed into wild-type M2 and YML081W-null strains. Three independent transformants for each reporter were grown to log phase, and assayed for β-galactosidase activity. Truncation of the reporter resulted in progressively lower activity levels. Importantly, cells lacking Yml081Wp produced significantly lower β-galactosidase activity than their wild-type counterparts (except for the shortest reporter fragment), suggesting that this transcription factor plays a positive role in stimulating ALD6 transcription. (C) A consensus binding site at −590 plays an important role in mediating Yml081Wp transcriptional activity on the ALD6 promoter. A reporter plasmid carrying a mutation of the YML081W consensus binding site was constructed for comparison to its wild-type counterpart. In cells producing normal levels of Yml081Wp, the mutation resulted in a 54% reduction in β-galactosidase activity (* indicates p<0.05 for a two-tailed Student t-test, compared to wild-type). However, in cells lacking Yml081Wp, the mutation had no significant effect on β-galactosidase activity. This result suggests that the consensus binding site at position −590 mediates Yml081Wp transcriptional activity on the ALD6 promoter.