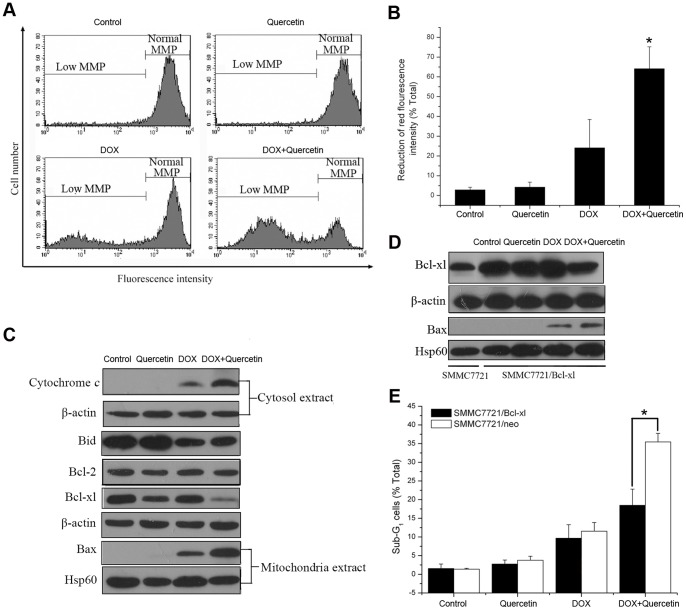
Figure 3. Quercetin potentiates DOX-induced apoptosis in liver cancer cells through Bcl-xl/Bax-mediated mitochondrial pathway.
(A, B) Effect of DOX and/or quercetin on the mitochondrial membrane potential breakdown in SMMC7721 cells treated with DOX (1 µM) and/or quercetin (20 µM) for 24 h. JC-1 is observed as green fluorescing monomers in the cytosol or as red fluorescing aggregates in intact mitochondria. The reduction of red fluorescence intensity indicates mitochondrial breakdown with intact membrane potential. *P<0.01 vs. DOX-treated cells. (C) Western blot analysis of the total expression of Bid, Bcl-2, and Bcl-xl, as well as the mitochondrial distribution of Bax and the cytosol distribution of cytochrome c in SMMC7721 cells treated with DOX (1 µM) and/or quercetin (20 µM) for 24 h. β-actin was used as an internal control for the total protein and cytosol protein. Hsp60 was used as an internal control for the mitochondrial protein. (D) Western blot analysis of the mitochondrial distribution of Bax and the total expression of Bcl-xl in SMMC7721 cells transfected with Bcl-xl expression vector and treated with DOX (1 µM) and/or quercetin (20 µM) for 24 h. (E) Effect of DOX and/or quercetin on the apoptosis of SMMC7721/Bcl-xl and SMMC7721/neo cells assayed by PI staining after DOX (1 µM) and/or quercetin (20 µM) was administered for 24 h. *P<0.01, SMMC7721/neo vs. SMMC7721/Bcl-xl cells. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments.