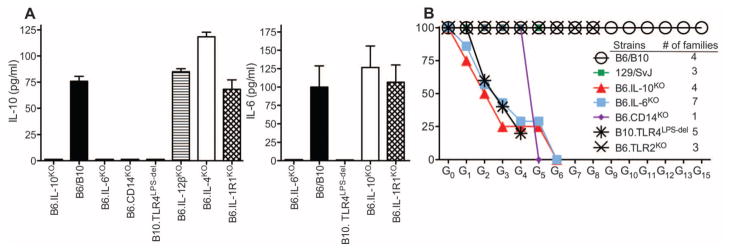
Fig. 4.
Genetic delineation of the immune subversion pathway induced by MMTV-LPS triggering of TLR4. (A) Splenocytes from B6 or B10 wild-type (used interchangeably), or from indicated knockout or mutant mice were incubated with an MMTV-SPF isolate followed by detection of IL-6 and IL-10 in supernatants by ELISA. Three to five mice were used per group. Graphs show means ± SEM. (B) Virus elimination in subsequent generations of mice with deficiencies within the immune sub-version pathway. G0 mice were fostered by SPF MMTV(LA)-infected C3H/HeN females. At least three animals per family were analyzed for hallmarks of infection: deletion of SAg-cognate T cells, viral RNA in the milk (table S1 and fig. S8A), and integrated proviruses in spleens (fig. S8B). A family that eliminated the virus was allowed to produce the next generation of mice, which was also tested to confirm virus loss. MMTV(LA)-infected B6 and B10 mice were used as controls. To control for background modifiers, 129/SvJ mice were also included, as many targeted knockout mice were originally generated on the 129/SvJ background.