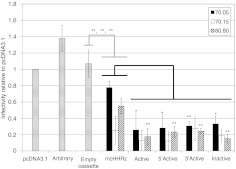
Figure 3.
Aptamer-mediated human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) inhibition in a single-cycle infectivity assay: extended hammerhead ribozymes (eHHRz) aptamer-expression constructs display increased inhibition as compared to the mcHHRz aptamer-expression constructs. 293FT cells were transfected with aptamer-expression constructs or controls (pcDNA3.1, arbitrary RNA, or empty cassette) followed 4 hours later by cotransfection of pNL4-3-CMV-EGFP and pMD-G. Virus was collected and infectivity was determined as in Figure 1b. The controls, “arbitrary RNA” and “empty cassette”, shown as bars with horizontal lines, represent averages of data obtained for the two indicated control fragments inserted into each of the five expression contexts (mcHHRz, Active, 5′Active, 3′Active, and Inactive). One-way ANOVA and Student's t-test were used to determine statistical significance between samples (*P <0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). Statistical comparisons to arbitrary RNA (gray lines) and to mcHHRz (black lines) were considered separately. Values are shown as the mean ± SD for three experiments. CMV, cytomegalovirus; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein.