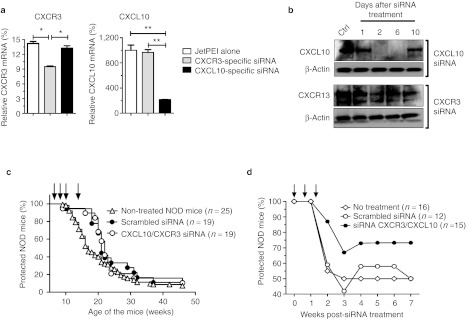
Figure 4.
CXCL10- and CXCR3-specific siRNA treatment reduces T1D incidence in CY-induced diabetes but not wild-type NOD mice. (a) Quantitative analysis of transcript levels of CXCR3 and CXCL10 expressed by pancreas-associated macrophages, relative to housekeeping gene, determined by qRT-PCR after CXCL10- or CXCR3-specific siRNA treatment. Prediabetic NOD mice (9 weeks of age) were injected with cyclophosphamide (CY) and subsequently treated with JetPEI alone or complexed with CXCL10- or CXCR3-specific siRNA (day 9 after CY injection). CXCL10 and CXCR3 relative mRNA levels were measured on 48 hours post-siRNA treatment. Results are presented as percentage compared with control. Error bars indicate mean ± SD, n = 3 experiments; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (b) Western blot analysis to assess the kinetics of CXCR3 and CXC10 downregulation. Total protein was extracted from pancreas-associated CD11b+ cells of NOD-CY–treated mice at 1, 2, 6, and 10 days after a single intraperitoneal injection of either CXCL10 or CXCR3 siRNA complexed with JetPEI on day 0. Fifty microgram per lane of total protein from untreated (Ctrl) and treated NOD mice was loaded. Staining of the indicated proteins on parallel blots is shown. Equal loading of tissue extracts was controlled by β-actin protein staining. Nonviral in vivo delivery of CXCR3/CXCL10 or scrambled control siRNA in (c) prediabetic wild-type or (d) CY-injected NOD mice. Data represents the cumulative diabetes incidence obtained from three independent experiments, n = 12–25 mice per group. Each single injection is shown with a black arrow on the graphs. Ctrl, control; mRNA, messenger RNA; NOD, nonobese diabetic; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription-PCR; siRNA, small interfering RNA;T1D, type 1 diabetes.