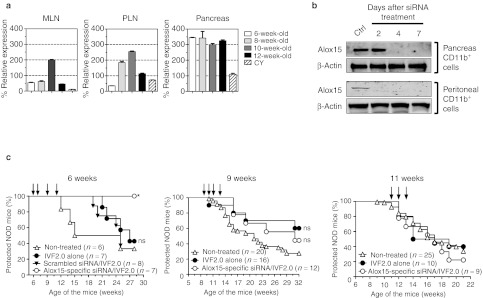
Figure 5.
Early treatment with Alox15 siRNA (siAlox15) prevents T1D in NOD mice. (a) Changes in Alox15 gene expression were assessed by qRT-PCR in the pancreas, mesenteric, and pancreatic lymph nodes (MLN and PLN) collected either from wild-type NOD mice at different time points during T1D pathogenesis (6, 8, 10, and 12 weeks of age) or day 7 after intraperitoneal cyclophosphamide (CY; 250 mg/kg of body weight) injection in 8-week-old NOD mice. Results are presented as percentage compared with control. Data are representative of three independent experiments and represent the mean ± SD, n = 6. (b) Western blot analysis for treated NOD mice at different time points. Total protein was extracted from pancreas or peritoneal CD11b+ cells of NOD mice at 2, 4, and 7 days after a single intraperitoneal injection of siAlox15/IVF2.0 complex on day 0. Ten microgram per lane of total protein from untreated (Ctrl) and treated NOD mice was loaded. The intensity of both Alox15 and β-actin (loading control) signals is showed. (c) Diabetes incidence in NOD mice treated with IVF2.0 alone or complexed with Alox15-specific or scrambled siRNA. Short-course treatments started either at 6, 9 or 11 weeks of age and each single injection is shown with a black arrow on the graphs.*P = 0.0109 and ns, not significant. Ctrl, control; NOD, nonobese diabetic; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription-PCR; siRNA, small interfering RNA; T1D, type 1 diabetes.