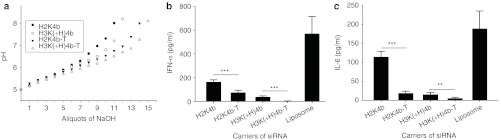
Figure 6.
Histidine-rich tails on HK peptides reduced cytokine levels in vivo. Two peptides, H2K4b-T and H3K(+H)4b-T, with eight additional histidines attached to the C-terminal lysine core, were compared with the parent peptides, H2K4b and H3K(+H)4b. (a) Before testing their ability to induce cytokine in vivo, the buffering capacity of these histidine-rich HK peptides and their parent HKs were tested. These peptides in complex with VEGFR-2 siRNA were injected into Balb/c mice with cytokine measurements measured 6 hours later. (b,c) H2K4b-T and H3K(+H)4b-T polyplexes induced cytokines (IFN-α (in b); IL-6 (in c)) significantly less than H2K4b and H3K(+H)4b polyplexes. Vehicle alone values: IFN-α 2.1; IL-6, 4.3 pg/ml. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, H2K4b versus H2K4b-T; H3K(+H)4b versus H3K(+H)K4b-T (t-test). The titration curves represent the mean of two independent experiments. HK, histidine-lysine; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; siRNA, small interfering RNA; VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2.