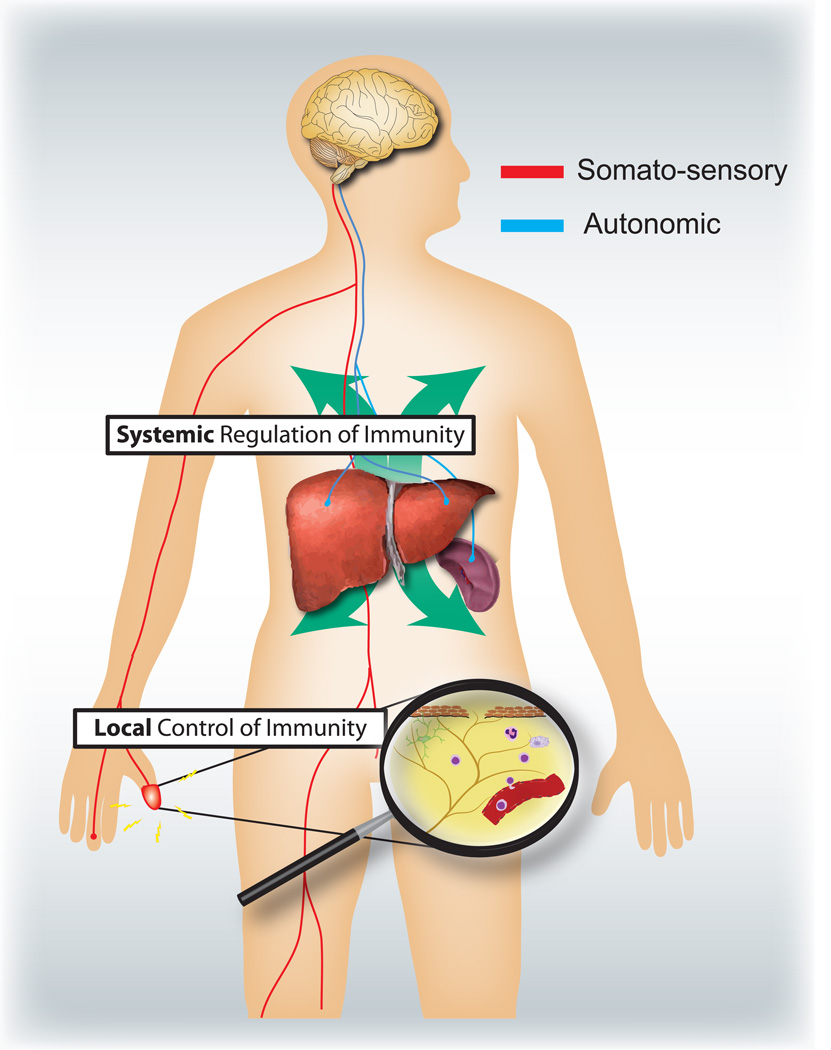
Figure 4.
Sensory and autonomic nervous systems modulate local and systemic immune responses respectively. Nociceptors innervating epithelial surfaces (e.g. skin and lung) induce localized inflammatory responses, activating mast cells and dendritic cells. In allergic airway inflammation, dermatitis and rheumatoid arthritis, nociceptor neurons play a role in driving inflammation. By contrast, autonomic circuits innervating the visceral organs (e.g. spleen and liver) regulate systemic immune responses by blocking macrophage and NKT cell activation. In stroke and septic endotoxemia, these neurons play an immunosuppressive role.