Figure 1.
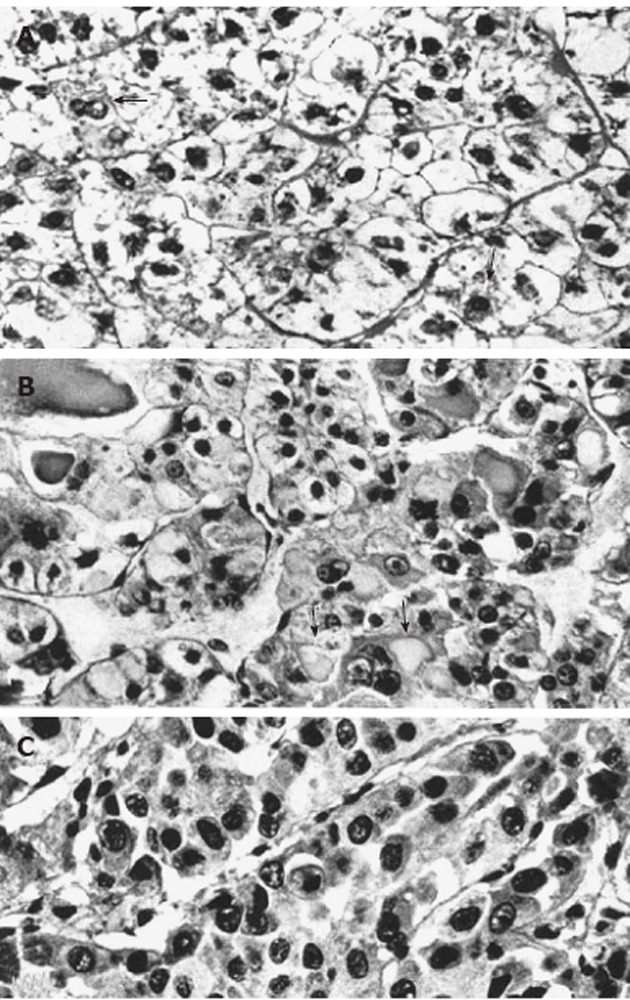
Light micrographs of portions from human hepatocellular neoplasms with and without glycogenosis. A: Clear-cell hepatocellular adenoma consisting predominantly of glycogenotic cells. In some cells (arrows) there is a reduction of glycogen and focal increase in cytoplasmic basophilia; B: Highly differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) composed of a mixed population of clear (glycogenotic) cells, acidophilic cells (ground-glass hepatocytes, arrows), and some glycogen-poor, basophilic cells; C: Poorly differentiated, glycogen-free, basophilic HCC. All: Hematoxylin and eosin stain, x 460, from Bannasch et al[6].
