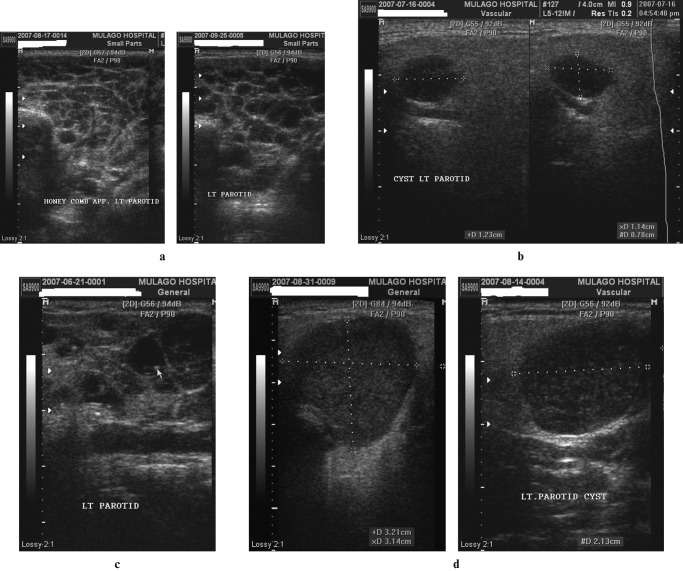
Figure 4.
(a) Lymphoepithelial cysts: honeycomb multicystic pattern. Transverse sections of the left parotid in a patient with bilateral parotid enlargement. There is a prominent honeycomb pattern formed by lymphoepithelial cysts of approximately the same size occupying almost all of the parotid gland substance. (b) Solitary lymphoepithelial cysts without internal mobile echoes (two images juxtaposed). Coronal sections of the left parotid in a patient with bilateral parotid enlargement. There are scattered solitary hypoechoic nodules seen with posterior acoustic enhancement. The largest cyst measures 11 × 12 × 8 mm, as shown by the electronic cursors. (c) Lymphoepithelial cysts with internal stationary echogenic foci. Coronal scan of a parotid demonstrating glandular tissue being replaced by cystic areas of varying sizes. Some of the cysts have septations whereas others have echogenic foci with posterior acoustic shadows. (d) Lymphoepithelial cysts with internal mobile echoes. Axial and coronal scans of the left parotid in a patient with bilateral parotid enlargement. There are multiple hypoechoic and heterogeneous cysts that exhibit posterior acoustic enhancement and multiple minute internal mobile echoes