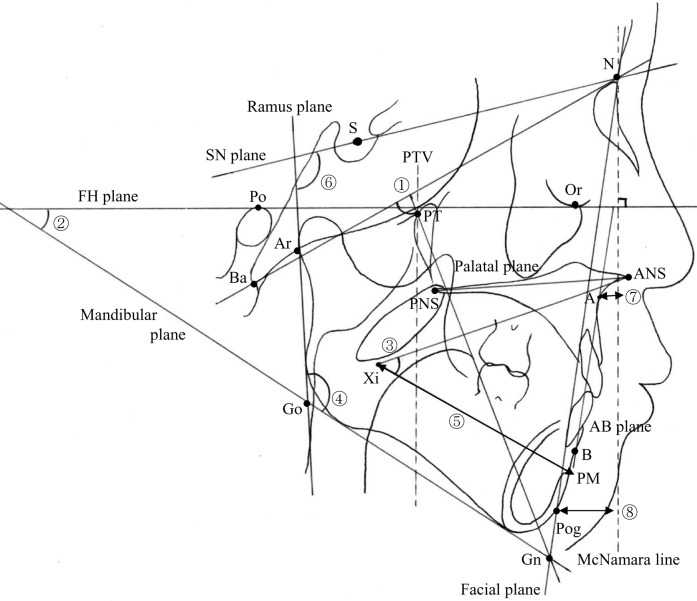
Figure 1.
Measurements of the craniofacial morphology. ◯1 Facial axis: the angle between the Pt (pterygoid point)–Gn (gnathion) point plane and the Ba (basion)–N (nasion) point plane; ◯2 mandibular plane angle: the angle between the frankfort horizontal (FH) plane and the mandibular plane; ◯3 lower facial height: the angle between the anterior nasal spine (ANS)–Xi (pterygomaxillary) point plane and the Xi–protuberance menti (PM) point plane; ◯4 gonial angle: the angle between the mandibular plane and the ramus plane; ◯5 corpus length: the distance between the Xi point and the PM point; ◯6 ramus plane to SN: the angle between the ramus plane and the SN plane [a line connecting the porion (S) and orbit (N) points]; ◯7 point A: the perpendicular distance to the McNamara line from the A point; ◯8 point Pog: the perpendicular distance to the McNamara line from the Pog point; anteroposterior dysplasia indicator (APDI): the total of the facial depth and the A–B plane angle (the angle between the FH plane and the A–B plane) and the palatal plane angle (the angle between the FH plane and the palatal plane)