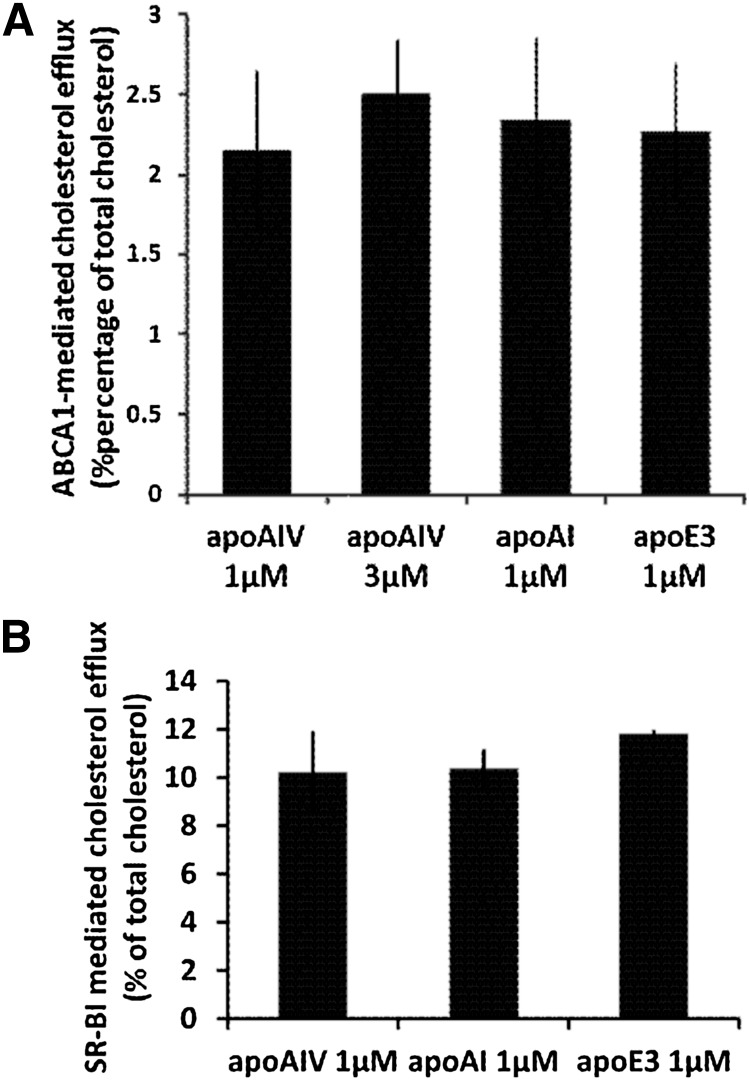
Fig. 1.
A: ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux from HEK293 EBNA-T cells transfected with an ABCA1-expressing plasmid using human apoA-I, apoE, and apoA-IV as cholesterol acceptors. Cholesterol efflux was determined as described in Experimental Procedures. The concentration of the acceptor apoA-IV in the medium was 1 μM or 3 μM and the concentration of apoA-I and apoE was 1 μM as indicated. The net efflux was calculated by subtracting the efflux obtained in the untransfected HEK293 EBNA-T cells from that of ABCA1-transfected cells. The difference in the net efflux promoted by apoA-IV, apoA-I, or apoE3 was not statistically significant. B: SR-BI-mediated cholesterol efflux from IdlA[mSR-BI] CHO cell line expressing the murine SR-BI (42), using rHDL-containing human apoA-I, apoE3, and apoA-IV as cholesterol acceptors. The concentration of each acceptor apolipoprotein bound to rHDL in the medium was 1 μM. The net efflux was calculated by subtracting the efflux obtained in the untransfected IdlA CHO cells from that of IdlA[mSR-BI] CHO cells. Values are the means ± SE from three experiments performed in duplicate. The difference in the net efflux promoted by rHDL-A-IV, rHDL-A-I, and rHDL-E3 was not statistically significant.