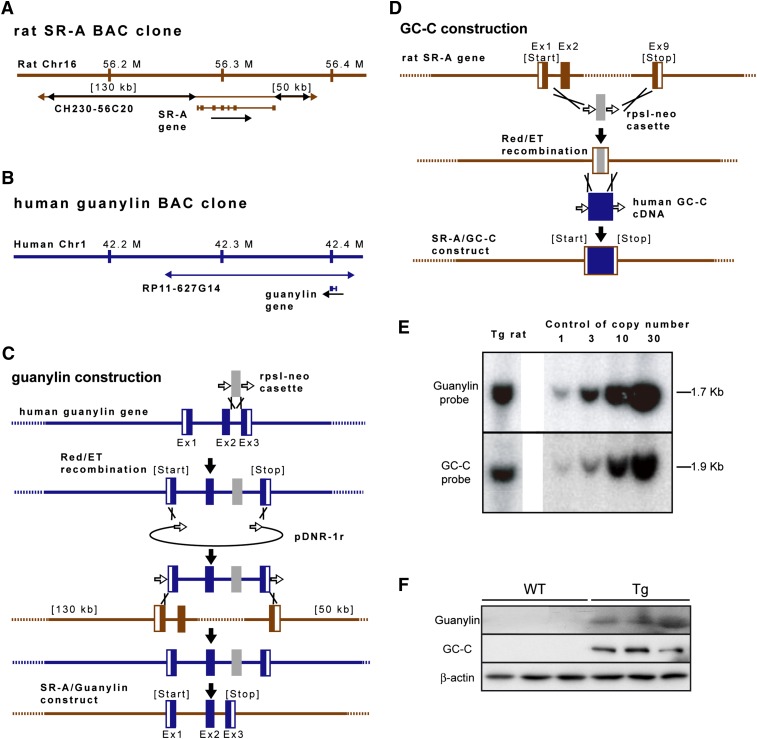
Fig. 2.
Generation of guanylin-GC-C BAC transgenic (Tg) rats. Structures of the (A) rat SR-A (CH230-56C20) and (B) human guanylin (RP11-627G14) BAC clones. Each BAC clone contains the full-length coding sequence and the 5- and 3-flanking sequences. (C, D) Schematic diagram of transgene construction. By using Red/ET recombination, the coding region of the rat SR-A gene was replaced with either (C) the entire human guanylin gene or (D) the human GC-C cDNA fragment. Ex, exon. (E) Southern blot analysis of guanylin-GC-C double-Tg lines. Hybridization with a radioactive probe showed that the BAC-transduced human guanylin and GC-C sequences were detected as a 1.7 kb PstI fragment and a 1.9 kb Dra I fragment, respectively. The copy number of each integrated transgene was determined through comparison with the intensity of a control signal (right panel). (F) Western blot analysis of the protein levels of guanylin and GC-C in the mesenteric fat tissues of male Tg and WT rats fed standard chow. β-actin was used as a loading control.