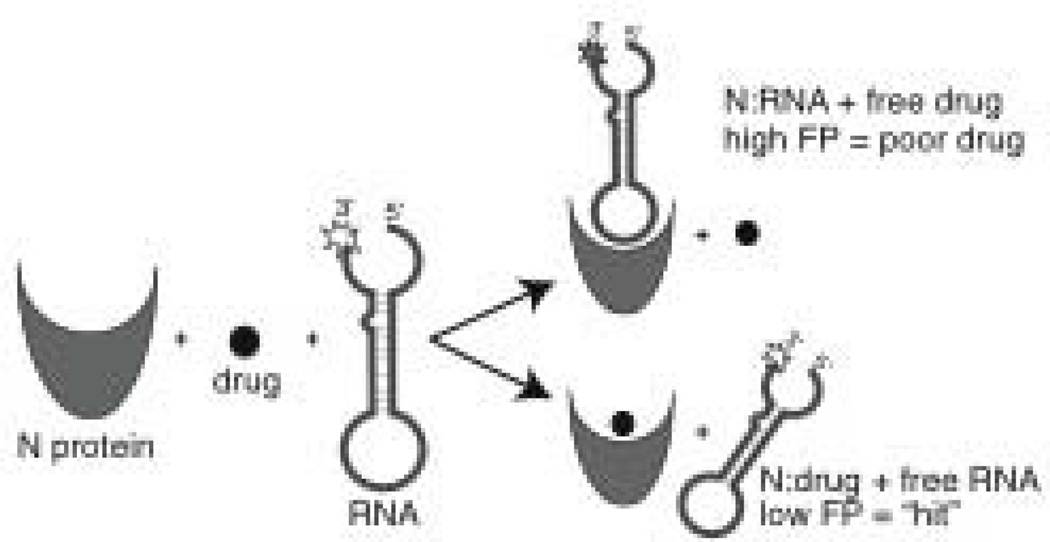
Figure 1. High throughput screening methodology.
Schematic diagram of the technique used to identify compounds that inhibit RNA binding to N protein in vitro. N was loaded into 384 well microplates, drug compound was added and then fluorescently labeled RNA. After a one hour incubation, fluorescence polarization (FP) measurements were taken. A high FP signal indicates that the compound was unable to prevent the RNA from binding N protein and would not be considered a potential antiviral drug. A low FP signal is indicative of a compound that inhibits the N-RNA interaction. Experimental wells that exhibit a low FP signal are considered “hits” and the compounds in those wells could be good drug candidates. Hits identified during the initial screen are subjected to further testing and verified in follow up assays.