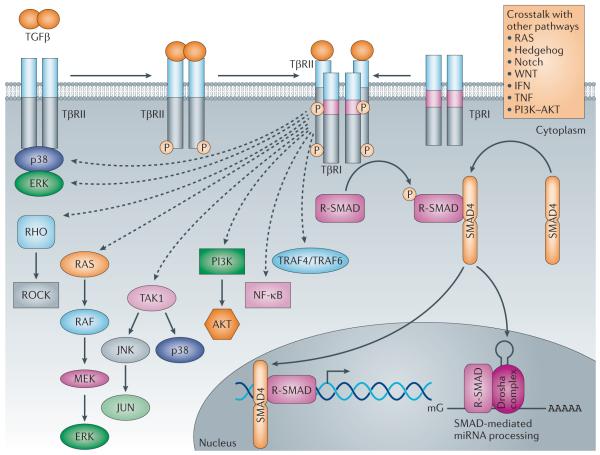
Figure 2. Schematic representation of non-canonical TGFβ signalling and crosstalk with other signalling pathways.
In the non-canonical pathways, the activated transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) receptor complex transmits a signal through other factors, such as TNF receptor associated factor 4 (TRAF4) or TRAF6, TGFβ-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), RHO, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-AKT, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), JUN N-terminal kinase (JNK) or nuclear factor-KB (NF-kB). TGFβ signalling can be influenced by pathways other than the canonical and non-canonical TGFβ signalling pathways, such as the WNT, Hedgehog, Notch, interferon (IFN), tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and RAS pathways. The crosstalk between TGFβ and other pathways defines the activities of TGFβ to propagate spatial- and temporal-specific signals. miRNA, microRNA; ROCK, RHO-associated protein kinase; R-SMAD, receptor-specific SMAD; TpR, TGFβ receptor. ‘mG’ and ‘AAAAA’ represent 5′ capping and 3′ polyadenylation of mRNAs, respectively.