Figure 1.
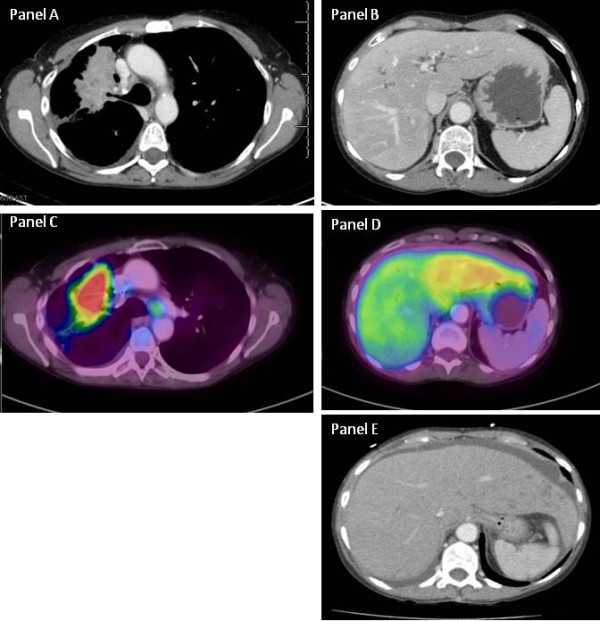
Case 2: Computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography. Panel A: Computed tomography of the chest shows the primary lesion in the right upper lobe caused by partial obstruction of the right upper lobe bronchus. Panel B: The CT scan of the liver shows essentially a normal-appearing liver without focal infiltrates present. Panel C: Positron emission tomography scan of the primary lesion shows intense fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake with some uptake noted in lymph nodes. Panel D: The right lobe of the liver looks normal, whereas the left lobe shows diffuse low FDG uptake suggestive of a pathological process. Panel E: A homogenous liver.
