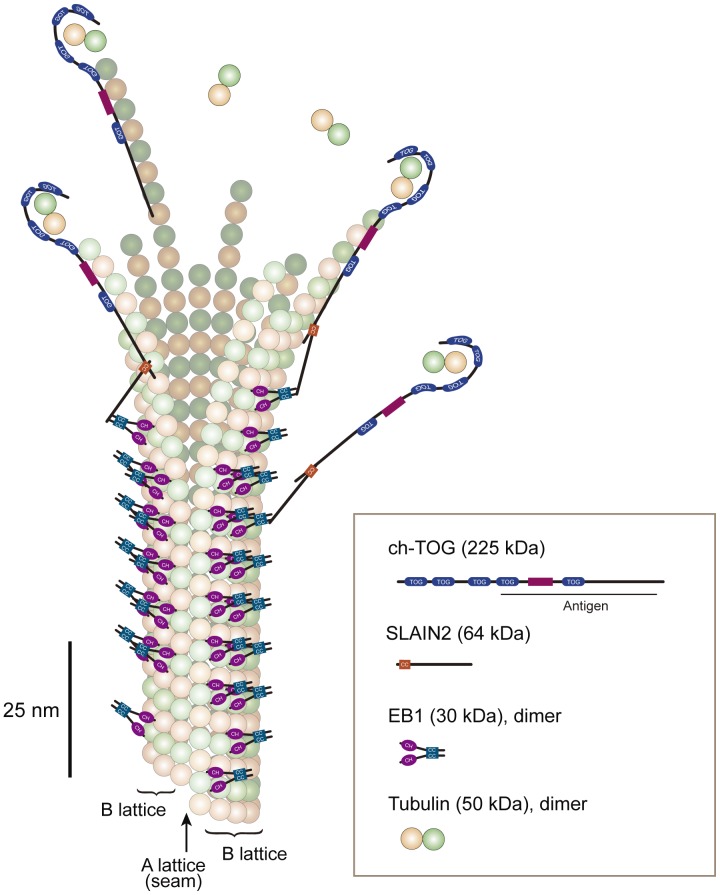
Figure 11. Model of the binding sites for EB1 and ch-TOG.
EB1 and ch-TOG are displayed on a graphic of a growing microtubule structure. The shape of the tubulin/ch-TOG complex was adapted from ref. [3]. XMAP215, which has a similar domain structure to ch-TOG, is a long molecule of ∼60 nm [55] that binds small tubulin oligomers [46] or one free tubulin dimer [3] at its NH2-terminus. The antibody against ch-TOG was generated using the COOH-terminal half of this molecule [28]. EB1 binds to the closed B lattice of the microtubule wall [56]. The microtubule tip probably contains protofilaments of different lengths. Based on our observation that the peak intensity of ch-TOG and EB1 comets was separated by ∼100 nm, the longer protofilaments for which growth is accelerated by ch-TOG [47] are assumed to consist of ∼12 tubulin dimers. SLAIN proteins may recruit ch-TOG to EB1 comets to increase the local concentration of ch-TOG.