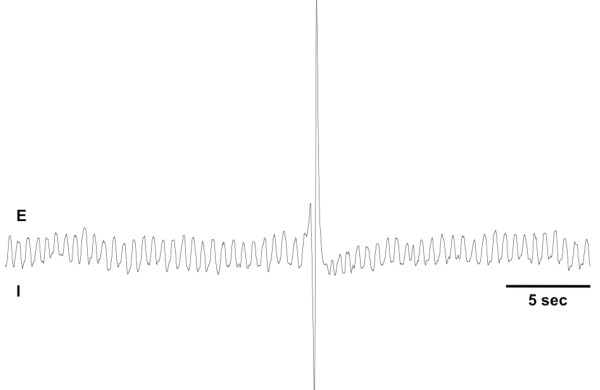
Figure 1.
A representative trace of coughing evoked by a citric acid challenge to an awake guinea pig is depicted. Inspiratory (I) efforts produce a negative pressure in the chamber, with expiratory (E) efforts producing positive pressures. These traces were used to measure respiratory rate at the outset of each experiment (breaths/ min), the time to first cough following initiation of the citric acid challenges, the Peak to Peak (P-P) pressures associated with cough (measured by comparing the P-P pressures associated with coughing, expressed as a percentage of the P-P pressures measured at eupnea), the total number of coughs evoked by each dose of citric acid and the total number of coughs evoked cumulatively by all doses of citric acid studied.