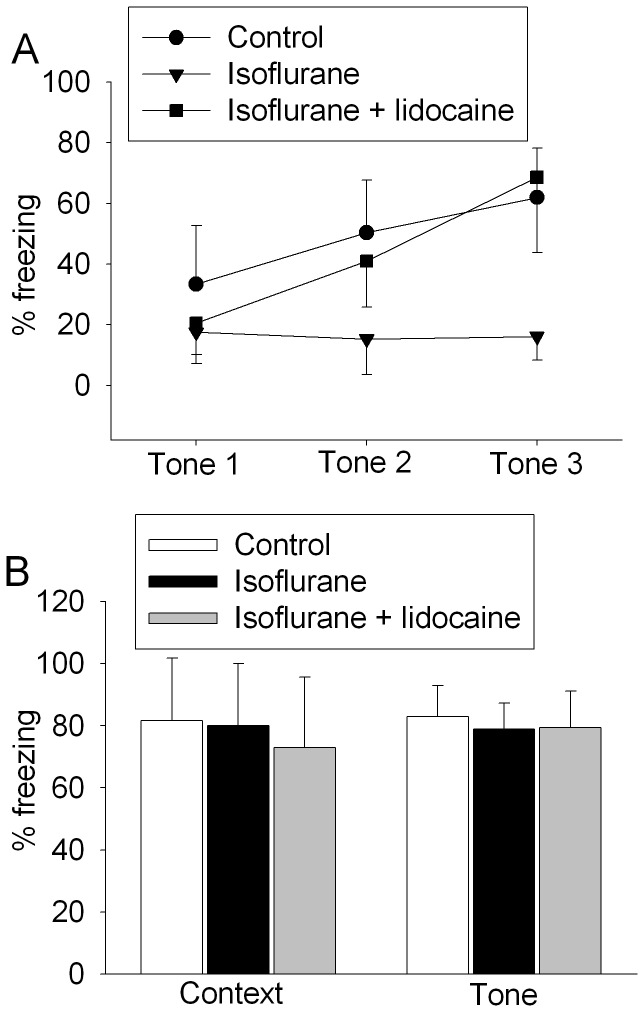
Figure 2. Isoflurane-induced learning impairment measured by fear conditioning test.
A: freezing behavior during training sessions for 18-month old Fisher 344 rats that were exposed to isoflurane in the presence or absence of lidocaine 27 days ago. Results are means±S.D. (n = 6 for control and isoflurane only groups and = 7 for isoflurane plus lidocaine group). There is a significant effect of training trial (P<0.001, among the control animals and animals exposed to isoflurane plus lidocaine), isoflurane use (P = 0.002, control animals vs. animals exposed to isoflurane only) and lidocaine use (P = 0.003, animals exposed to isoflurane only vs. animals exposed to isoflurane plus lidocaine) on the freezing behavior. Statistical analysis was performed by two-way analysis of variance. B: freezing behavior during the context- and tone-related fear conditioning tests for 18-month old Fisher 344 rats that first had the training sessions and were exposed to isoflurane in the presence or absence of lidocaine at 30 min after the training sessions. Results are means±S.D. (n = 4 for control group and = 5 for the isoflurane only and isoflurane plus lidocaine groups).