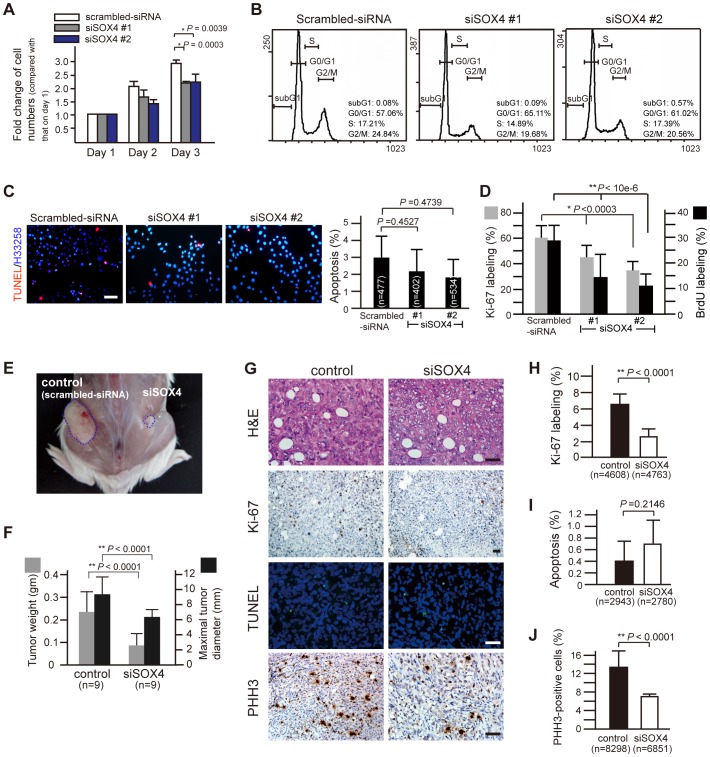
Figure 4. Reduced in vitro and in vivo tumor growth by SOX4 suppression.
(A) Cell proliferation is affected in PANC-1 cells with RNAi-suppression of SOX4. 30000 cells were seeded into each well in a 12-well plate. At 24, 48 or 72 hours after seeding, cells were harvested and counted by trypan blue exclusion assay. Error bars, SD from six independent experiments, Student's t-test. (B) Representative flow cytometry of siSOX4 cells stained with propidium iodide shows no significant variation from scrambled-siRNA cells in apoptosis (depicted by sub-G1) or in cell cycle progression. The percentage of cells in sub-G1, G0/G1, S and G2/M phase was shown at the right downward corner of each plot. (C) representative TUNEL-labeling of cells challenged by the genotoxic agent cisplatin (10 µg/ml, 12-h). Differences in apoptosis was not observed between SOX4-knockdown (siSOX4#1 and siSOX4#2) and control (scrambled-siRNA) cells. (D) lower cell proliferation rate and decreased number of cells staying at M phase in siSOX4 cells. siSOX4 and scrambled-siRNA cells were plated on coverslips and incubated for 48 hours. Before harvest and fixation with paraformaldehyde, cells were incubated with 10 µM of BrdU for 3 hours and were then subjected to anti-Ki-67 or anti-BrdU immunofluorescent staining. Twenty randomly selected high power fields (x400) were counted for statistical analysis (Student's t-test). (E) Tumor xenograft of siSOX4/PANC-1 cells grows smaller than that of control cells (scrambled-siRNA) in a SCID mouse. The mice were sacrificed 30 days after subcutaneous inoculation of the control cells on the left and the siSOX4 cells on the right side of the flank. (F) Smaller and lighter tumor xenografts of siSOX4 cells compared to those of control (n = 9, Student's t-test). (G) representative H&E, Ki-67, PHH3 immunostain, and TUNEL labeling in tissue sections from tumor xenografts. Scale bars = 50 µm. (H, I, and J) quantification of proliferation (Ki-67 labeling), apoptosis (TUNEL stain) and mitosis (PHH3-immunostain). Eighteen randomly selected fields (x200) in each Ki-67-stained section and cells in twenty-seven randomly selected fields (x400) for TUNEL labeling or PHH3 immunostain were counted in each xenograft tumor. The proliferating index and the mitotic counts of siSOX4 tumor cells are significantly lower than that of control cells, while the percentage of apoptotic cells did not differ (Student's t-test). n, the total number of cells counted.