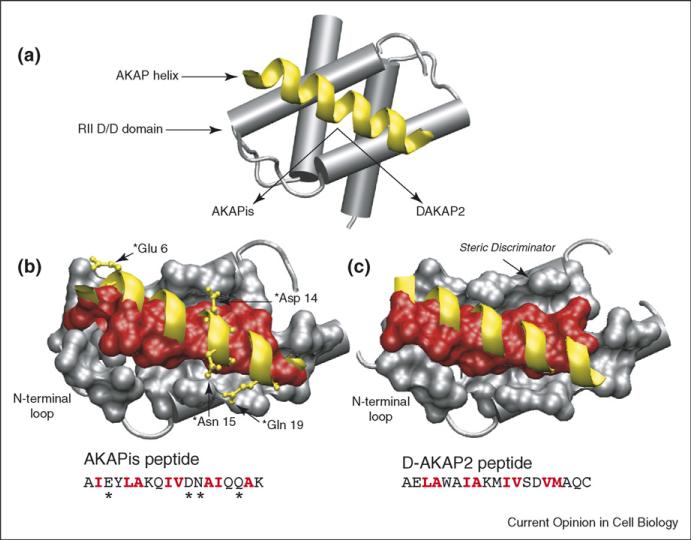
Figure 1.
Structure of the PKA/AKAP binding interface. (a) Schematic of an AKAP PKA-anchoring domain (yellow) bound to the D/D domain (residues 1–44) of RII. In the structures shown below, the helical backbones of AKAPis and DAKAP2 are depicted in yellow and residues that form the binding interface between RII and the AKAP (red) are shown in space-filling. The primary sequences of the AKAP peptides are included with interfacial residues highlighted in red. (b) Close-up of the AKAPis helix bound to the hydrophobic groove of RII. AKAPis residues that form polar interactions with RII are shown in ball and stick (yellow). (c) Close-up of the DAKAP2 PKA-anchoring domain bound to the hydrophobic groove of RII. The potential steric discriminator that contributes to the PKA-subtype specificity of AKAPs is indicated. Comparison of the two structures shows that, although they are quite similar, the RII/AKAPis binding interface comprises a greater number of residues and there are differences in the registry of the helical side-chains involved at each interface.