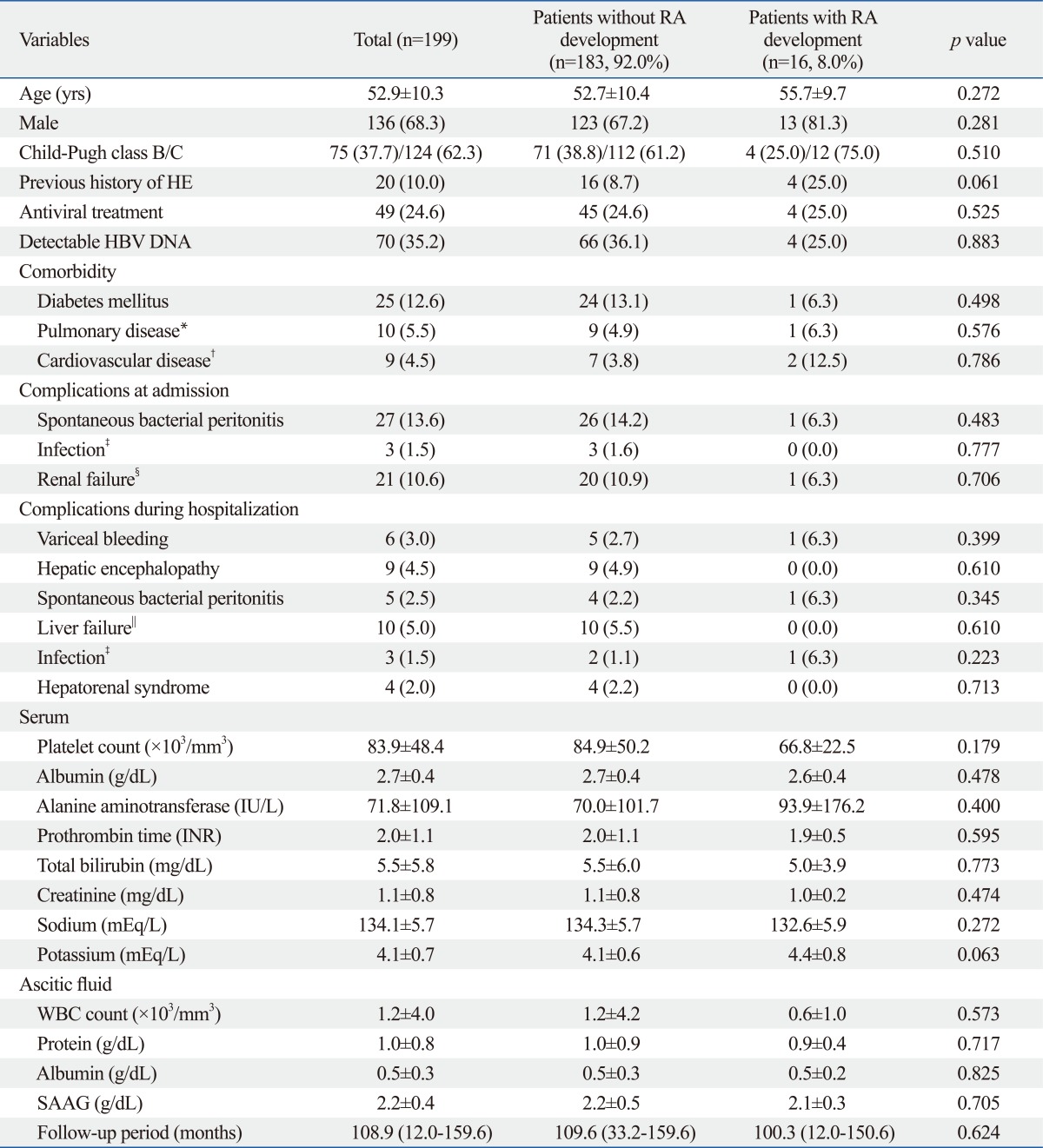
Table 1.
Baseline Characteristics of Patients with HBV-Related Liver Cirrhosis Who Were Hospitalized to Control Ascitic Decompensation at Admission (n=199)
HBV, hepatitis B virus; HE, hepatic encephalopathy; INR, international normalized ratio; WBC, white blood cell; SAAG, serum ascites albumin gradient.
Variables are expressed as mean±SD, median (range), or n (%).
*Pulmonary disease included pulmonary tuberculosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and asthma.
†Cardiovascular disease included hypertension and congestive heart failure.
‡Infection included pneumonia, urinary tract infection, and sepsis.
§Renal failure was defined as acute or chronic renal failure, but not hepatorenal syndrome.
∥Liver failure was defined as rapid deterioration of liver function results in coagulopathy, usually an INR greater than 1.5 and any degree of HE.