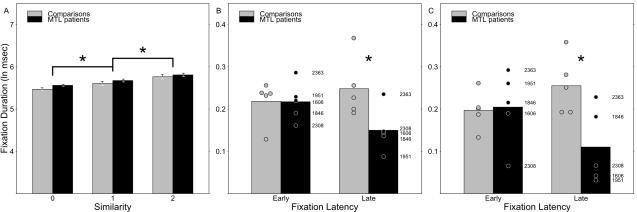
Figure 3.
Modulation of fixation duration by lure-sample similarity. Note that the y-axes of all three panels use ln(ms) units, but that (a) uses a different scale than (b) and (c), which both plot differences in fixation durations rather than whole fixation durations. (a) Both comparisons and MTL patients fixated items that resembled the sample for longer than those that did not. Whiskers indicate standard error of the mean. (b) and (c) However, as more fixations intervened between the last viewing of the sample item and the fixation of a given lure, this effect was attenuated in patients and exaggerated in comparisons; these plots illustrate the effect using the difference in fixation durations between 2- and 0-match lures early and late in search. Group means are presented as bars, while the difference observed for each subject is plotted as a point, and patient values are individually labeled for reference. (b) summarizes data from the entire experiment, while (c) summarizes data from only the first third of the experiment (i.e., 27 trials). * indicates reliable differences at p < 0.05: differences between levels of lure-sample similarity in (a); and reliable MTL status by latency interactions in (b) and (c).