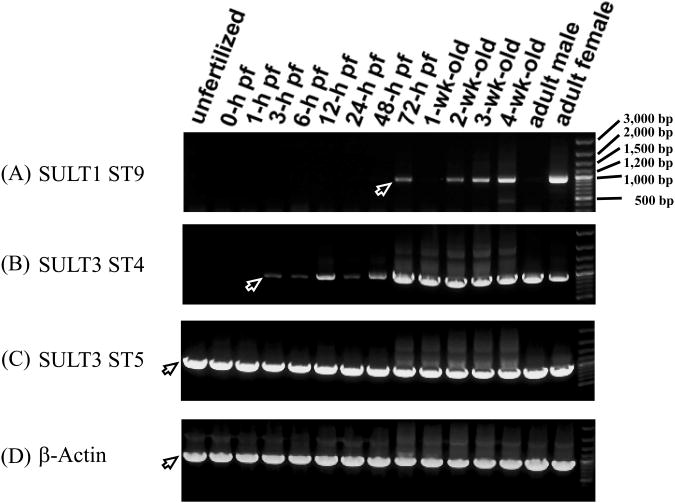
Figure 5.
Developmental stage-dependent expression of the zebrafish SULT1 ST9, SULT3 ST4 and SULT3 ST5. (A) - (C) RT-PCR analysis of the expression of mRNAs encoding SULT1 ST9, SULT3 ST4 and SULT3 ST5 at different stages during embryogenesis and larval development onto maturity. Final PCR mixtures were subjected to 0.9% agarose electrophoresis. Samples analyzed correspond to unfertilized zebrafish eggs, zebrafish embryos during the zygote period (0-hour post-fertilization (pf), cleavage period (1-hour pf), blastula period (3-hour pf), gastrula period (6-hour pf), neurula/segmentaion period (12-hour pf), pharyngula period (24-hour pf), and hatching period (48- and 72-hour pf), 1, 2, 3, 4-week-old zebrafish larvae, and 3-month-old adult male or female zebrafish. The positions of PCR products corresponding to different zebrafish SULT1 ST9, SULT3 ST4 or SULT3 ST5 cDNAs, visualized by ethydium bromide staining, are marked by arrows. (D) RT-PCR analysis of the expression of the zebrafish β-actin at the same developmental stages as those described above. The figure is representative of three independent repetitions with different samples.