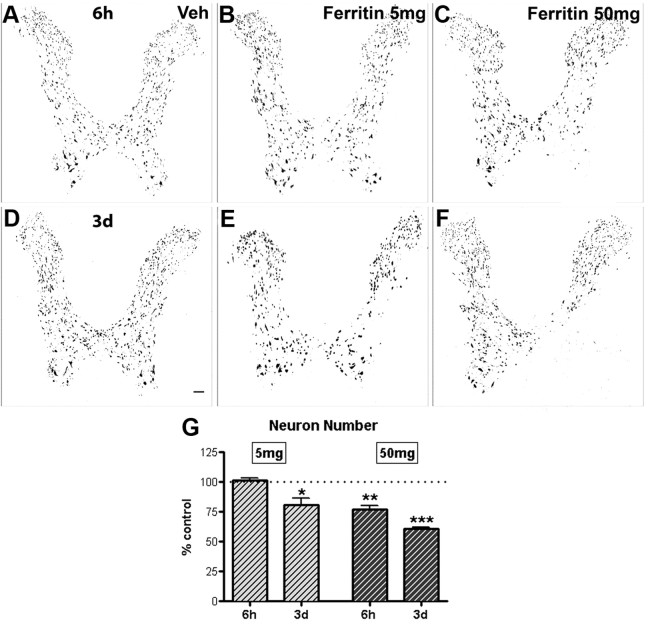
Figure 3.
Ferritin injection caused neurotoxicity. Neurons were identified with an antibody against NeuN and counted in the ipsilateral gray matter. A–C, Low-power views of gray matter 6 h after injection of vehicle (Veh; A), low-dose ferritin (B), or high-dose ferritin (C). Subtle neuron loss was evident in ventral horn of sections injected 6 h prior with high-dose ferritin (C). D–F, Low-power views of gray matter 3 d after injection of vehicle (D), low-dose ferritin (E), or high-dose ferritin (F). Between 6 h and 3 d, low-dose ferritin caused ∼20% neuron loss; during this same time, neuron loss had progressed in spinal cords receiving high-dose ferritin. G, Quantification of neurons in ipsilateral gray matter revealed a significant cell loss after microinjecting 5 mg (20% decrease at 3 d) and 50 mg of ferritin (25% decrease at 6 h and 40% decrease at 3 d). Data represent mean ± SEM and are expressed relative to vehicle control numbers, indicated by dotted line. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus vehicle control. Scale bar: (in D) A–F, 100 μm.