Figure 1.
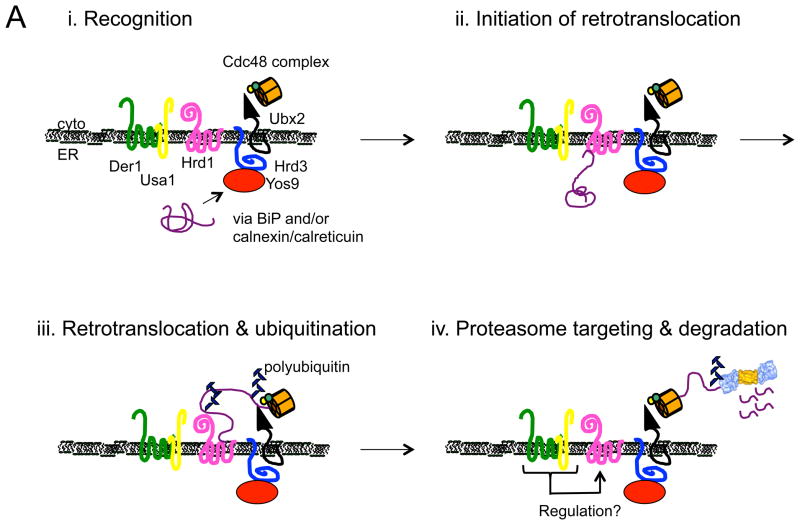
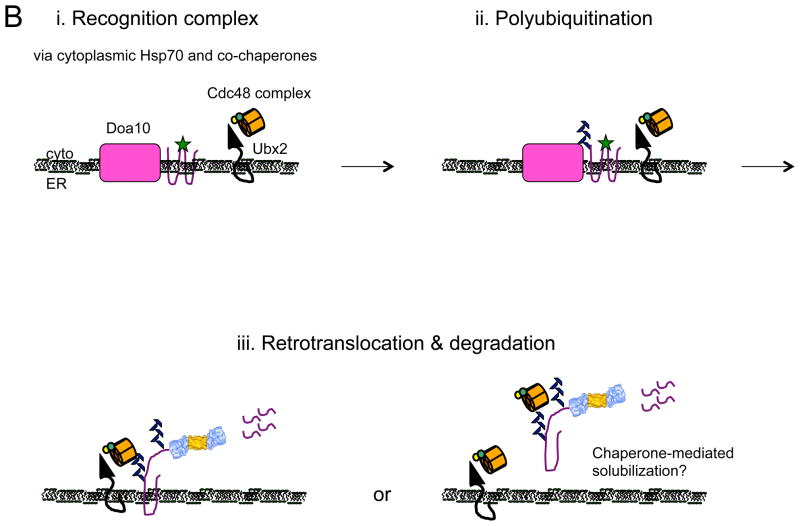
Models for the recognition, targeting, and degradation of (A) soluble and (B) integral membrane ERAD substrates. (A) The ERAD of soluble, lumenal substrates in yeast requires the action of the Hrd1 complex, whose members are depicted in this figure. Recognition (i) of a substrate by this complex follows selection by BiP and/or by lectins with chaperone-like properties (e.g., calnexin/calreticulin). Yos9 is also an ER lectin that binds to Hrd3 (SEL1 in higher eukaryotes), and lectins that act similarly in mammals include Os9 and XTP-3B. Hrd1 is most intimately linked to substrate retrotranslocation (ii) and ubiquitinates and delivers substrates to the Cdc48 complex, which harbors hexameric Cdc48 (p97 in mammals) and single copies of Ufd1 and Npl4 (iii). Cdc48 couples ATP hydrolysis with subsequent delivery to the proteasome (iv). Cdc48 may also help unfold and disaggregate substrates prior to degradation, and appears to be tethered to the ER via Ubx2. Der1 (Derlin-1, 2, and 3 in mammals) and Usa1 (the mammalian homolog is Herp) like function as Hrd1 regulatory factors. (B) During the ERAD of an integral membrane protein that contains a misfolded cytoplasmic domain (depicted with a green star), a substrate is recognized by cytoplasmic chaperones (i) and is then ubiquitinated by Doa10 (ii) in yeast. Doa10 contains 14 transmembrane segments and like Hrd1 has also been proposed to act as a retrotranslocation channel. The Cdc48 complex extracts and maintains the solubility of the ERAD substrate (iii), before or concomitant with proteasome-mediated degradation. Not shown are E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzymes, which are integral membrane proteins or are tethered to the membrane, as well as proteasome adaptors that aid in the final targeting of substrates to the proteasome. Also not shown is the pathway that leads to the degradation of a protein with a misfolded lesion residing in a membrane-spanning segment, a process that also requires Hrd1. The ubiquitin ligase activities of Hrd1 and Doa10 are mediated by the RING domain that resides in the cytoplasm. In both panels, the ERAD substrate is depicted in purple. See text for additional details and (Xie and Ng, 2010).