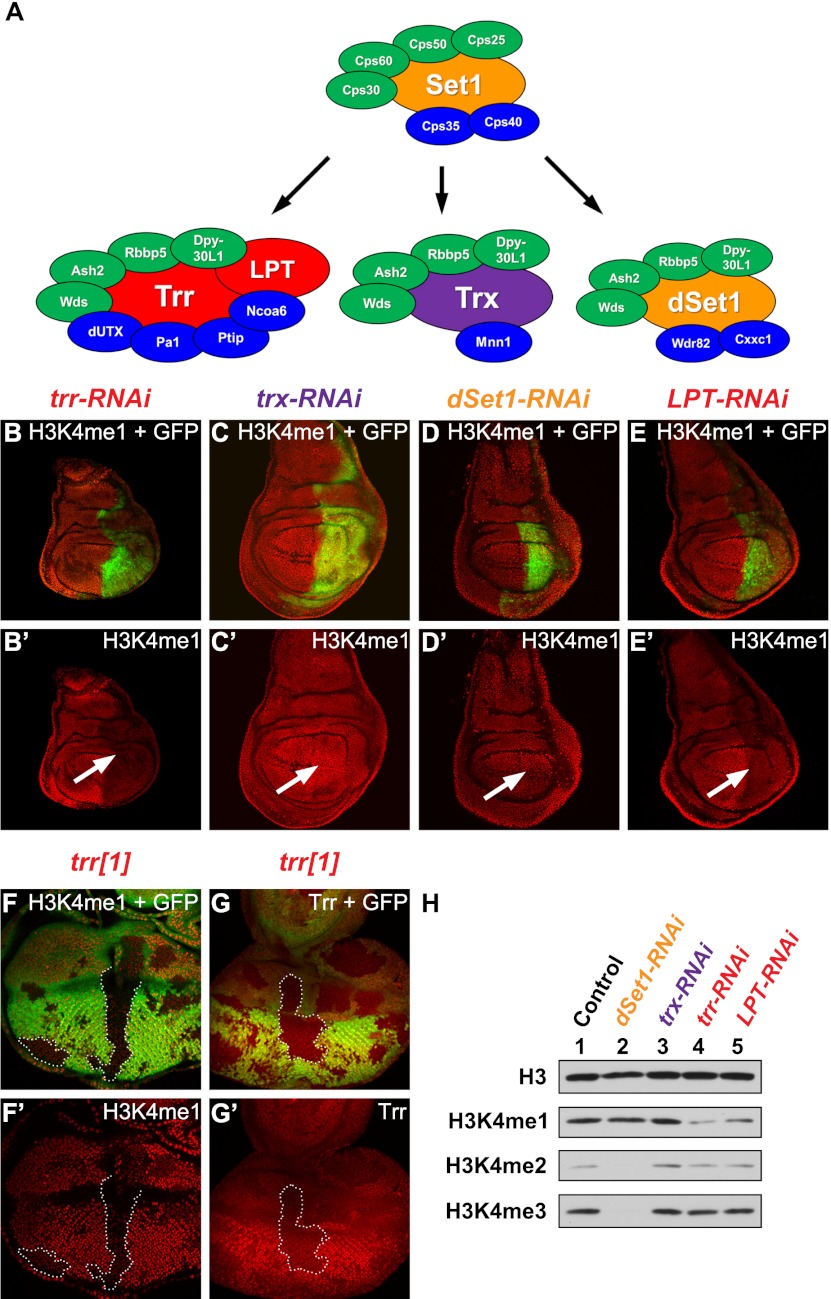
Figure 1.
The Drosophila Mll3/Mll4 homolog Trr is a major H3K4 monomethyltransferase in vivo. (A) The COMPASS family of H3K4 methyltransferase complexes in yeast and Drosophila (Mohan et al. 2011, 2012). Trr and LPT are highlighted in red, Trx is in purple, dSet 1 is in orange, core complex subunits are in green, and complex-specific subunits are in blue. (B–E) RNAi-mediated knockdown of Drosophila H3K4 methyltransferases in the posterior compartment of the wing imaginal disc. GFP expression in green marks the posterior part (highlighted by a white arrow in the antibody-only channel) where the knockdown occurs. Knockdown of Trr (B′) or LPT (E′) results in a global reduction of H3K4me1. No bulk changes in H3K4me1 were observed when Trx (C′) or dSet1 (D′) levels were reduced by RNAi. (F,G) Flipase-catalyzed induction of trr mutant clones (no GFP expression) with the eye-specific eyeless (ey) promoter. Wild-type tissue is marked in green (GFP expression). Representative trr mutant clones are outlined by white dashed lines. Mutant clones of trr1, a trr-null allele, display decreased levels of H3K4me1 (F′) and loss of Trr (G′). (H) Western blot of lysates from RNAi-treated Drosophila S2 cells. (Lane 1) Control lacZ-RNAi. (Lane 2) dSet1-RNAi. (Lane 3) trx-RNAi. (Lane 4) trr-RNAi. (Lane 5) LPT-RNAi. (Panel 1) α-H3. (Panel 2) α-H3K4me1. (Panel 3) α-H3K4me2. (Panel 4) α-H3K4me3. Genotypes used were as follows: UAS-Dcr-2/+; en-GAL4 UAS-EGFP/+; UAS-trr-RNAi/+ (B), UAS-Dcr-2/+; en-GAL4 UAS-EGFP/UAS-trx-RNAi (C), UAS-Dcr-2/+; en-GAL4 UAS-EGFP/UAS-dSet1-RNAi (D), UAS-Dcr-2/+; en-GAL4 UAS-EGFP/+; UAS-LPT-RNAi/+ (E), and trr1 FRT19A/ubi-GFP FRT19A; ey-FLP/+ (F,G).