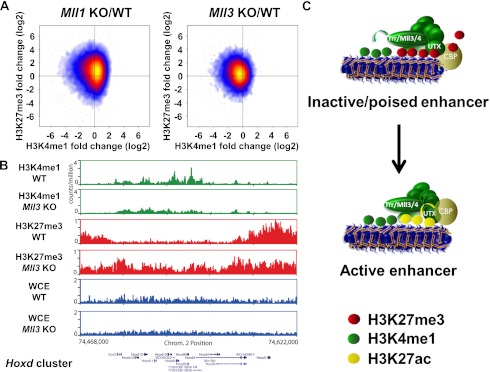
Figure 7.
The mammalian homolog of Trr, Mll3, is one of the major monomethyltransferases in mammalian cells. (A) Many promoter-distal elements (those H3K4me1 peaks not occurring within a gene) in Mll3 knockout (KO) MEFs exhibit a reduction in the H3K4me1 levels and an increase in H3K27me3 levels (right scatter plot), whereas Mll1 knockout MEFs display an increase in H3K4me1 and H3K27me3 levels (left scatter plot). The quotient of fold enrichment (immunprecipitation/whole-cell extract) in mutant MEFs versus wild-type (WT) MEFs was plotted for both the X-axis and Y-axis for H3K4me1 and H3K27me3, respectively. The scatter plot point density is indicated by color. (Blue) Low; (red) medium; (yellow) high. Mll1 and Mll3 wild-type and knockout MEFs were previously described in Hanson et al. (1999), Hughes et al. (2004), and Wang et al. (2009). (B) Decrease of H3K4me1 and increase of H3K27me3 over the Hoxd cluster in Mll3 knockout MEFs. Whole-cell extracts (WCE) represent the input chromatin. (C) Model describing the role of Mll3/4/Trr COMPASS-like complexes in the transitioning of enhancer activation. Mll3/4 in mammals and Trr in Drosophila participate in complexes joining the H3K27 demethylase UTX with the H3K4 monomethyltransferase activity of Mll3/4 and Trr to allow for H3K4me1 by the Trr/COMPASS and H3K27ac by CBP on enhancers. The transition to the active state of enhancers is promoted by activation of the Trr/Mll3/Mll4 COMPASS complex, which is able to achieve demethylation of H3K27me3 through UTX and H3K4me1 through Trr/Mll3/Mll4. CBP is activated via its interaction with UTX.