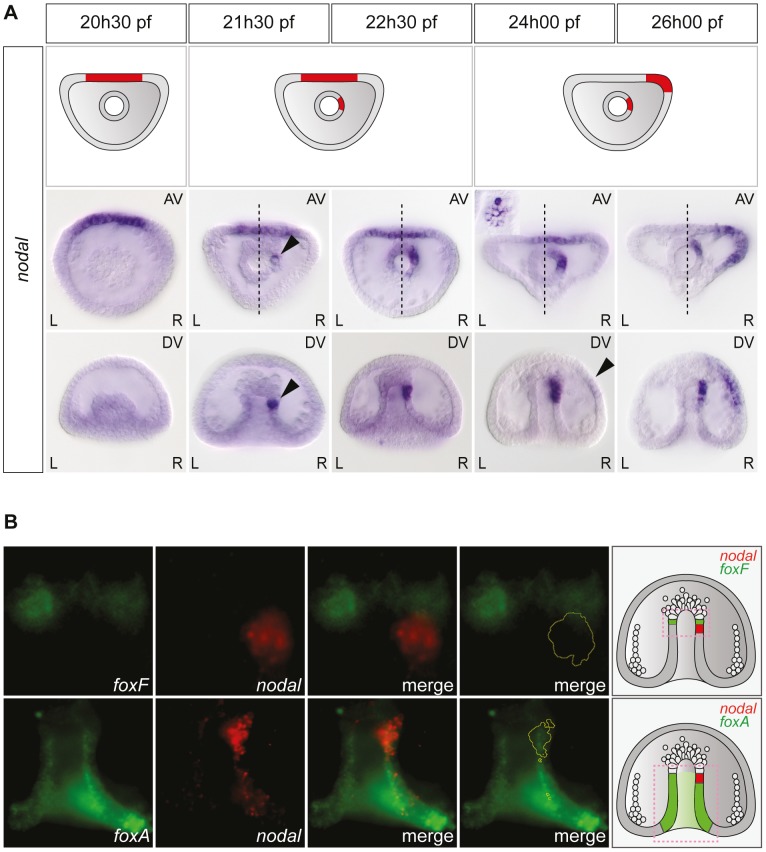
Figure 2. Left-right asymmetric expression of nodal is initiated in a discrete endodermal territory.
A, Whole-mount in situ hybridizations with a nodal probe. Asymmetric expression of nodal is first detected in the endoderm, several hours before the onset of asymmetric nodal expression in the ectoderm. AV, view from the animal pole; DV, view from the dorsal side; L, left; R, right. The black arrowheads highlight the beginning of nodal expression on the right side of the tip of the archenteron and in the ectoderm. The inset shows a high magnification view of the nodal expressing cells arranged in a rosette. B, Double fluorescent in situ hybridization with nodal (red) and either the endodermal marker gene foxA or the coelomic pouch marker gene foxF (green). The early expression of nodal is initiated in the endoderm territory underlying the coelomic pouch precursors that express foxF. The schemes on the right depict the territories expressing nodal (red) with respect to the mesodermal territory that expresses foxF and the endodermal territory that expresses foxA (green).