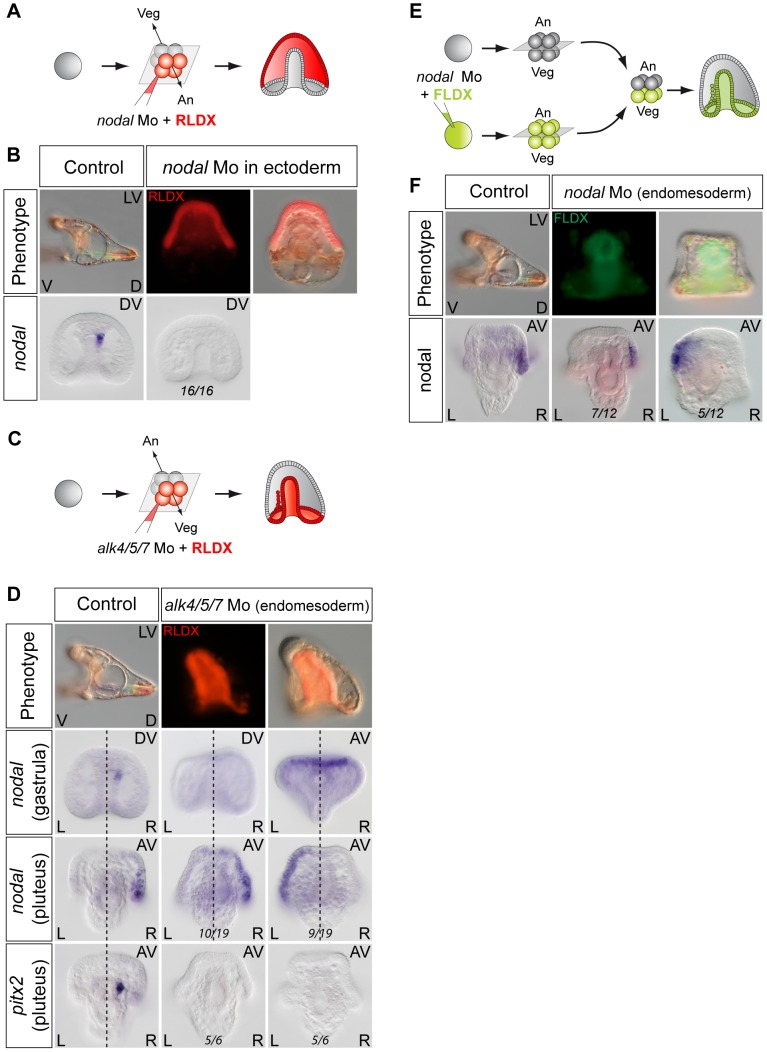
Figure 7. Establishment of left-right asymmetry requires reciprocal Nodal signaling between the ectoderm and endomesoderm.
A,B ectodermal Nodal signals are required for nodal expression in the endomesoderm. A, Experimental design. The four animal blastomeres of a 8-cell stage embryo were injected with a nodal morpholino and nodal expression was analyzed at the gastrula stage. B, DIC and Fluorescent images of injected larvae and whole mount in situ hybridization of injected embryos with the nodal probe. Blocking nodal mRNA translation in the ectoderm abolishes nodal expression in the endomesoderm at gastrula stage and radializes the embryos. C,D, nodal signaling in the endomesoderm is required for establishment of left-right asymmetry in the ectoderm. C, Experimental design. The vegetal half (four blastomeres) of embryos at the eight-cell stage were injected with the alk4/5/7 morpholino. D, DIC and Fluorescent images of injected larvae and whole mount in situ hybridization of embryos with the nodal probe. nodal is expressed on the right side of the ectoderm in control embryos but in 9 out of 19 injected embryos, nodal expression is detected on the left side. pitx2 is expressed on the right side of the endomesoderm in control embryos but in 5 out of 6 alk4/5/7 morpholino injected embryos, pitx2 expression is lost. E,F, Mosaic analysis using chimeric embryos produced by microsurgery. E, Experimental design. The vegetal half of a nodal morphant (green) was combined with a control animal half (grey). F, Fluorescent and DIC images of a chimeric larvae and whole mount in situ hybridization of chimeric embryos with a nodal probe. nodal is expressed on the right side of the ectoderm in control embryos but in 5 out of 12 chimeric embryos, nodal expression is detected on the left side. V, ventral; D, dorsal; LV, lateral view; AV, animal pole view; L, left; R, right; An, animal pole; Veg, vegetal pole.