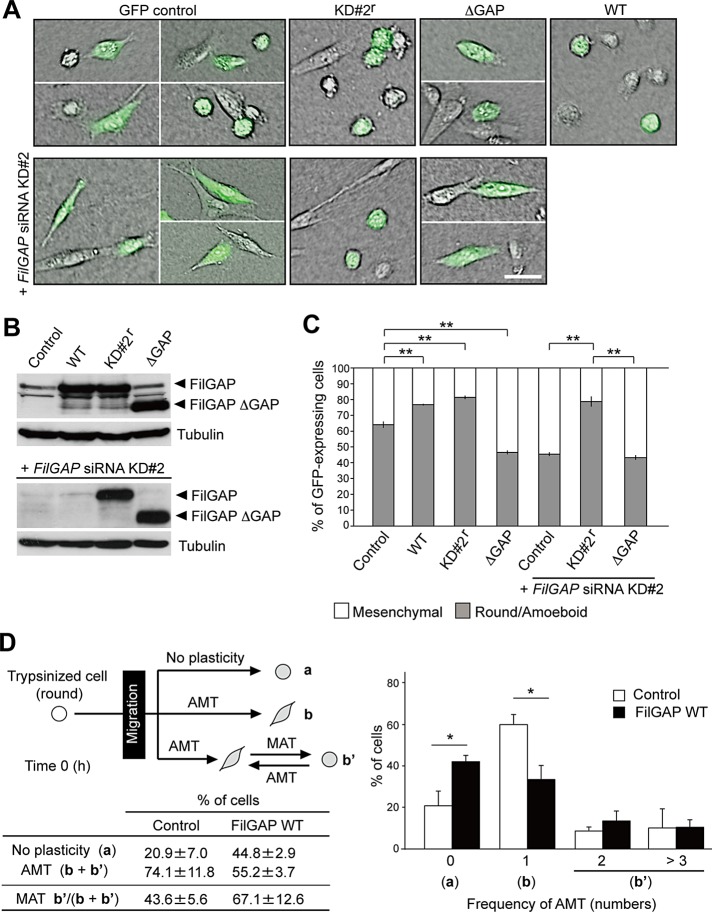
FIGURE 3:
FilGAP induces amoeboid morphology. (A) MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with a control plasmid (pIRES2-AcGFP), or pIRES2-AcGFP plasmids encoding wild-type FilGAP (WT), FilGAP resistant to siRNA KD#2 sequence (KD#2r), or FilGAP lacking its GAP domain (ΔGAP), and cultured on plastic plates for 24 h. For cotransfection of plasmid DNA and FilGAP siRNA KD#2, the cells were first transfected with siRNA for 24 h and then cotransfected with plasmid DNA; this was followed by an additional 24-h culture on plastic plates. The transfected cells were trypsinized and then plated on collagen gels. After 24 h, cells were fixed and GFP (green) was localized. Merged images of DIC and GFP are shown. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Forced expression of FilGAP constructs in cells that were cultured on plastic plates. FilGAP and tubulin (loading control) were detected by immunoblotting. (C) The morphology of GFP-expressing cells was categorized as mesenchymal or round/amoeboid. The data are the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments (n > 200 cells for each experiment). **, p < 0.01. Statistical significance was determined by Student's t test. (D) Time-lapse video microscopy analysis. MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with a control plasmid (pIRES2-AcGFP) or pIRES2-AcGFP-FilGAP (WT) and plated on collagen gels. Cells were monitored for 24 h and analyzed. The data are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (n = 20–30 cells counted for each experiment). *, p < 0.05. Statistical significance was determined by Student's t test.