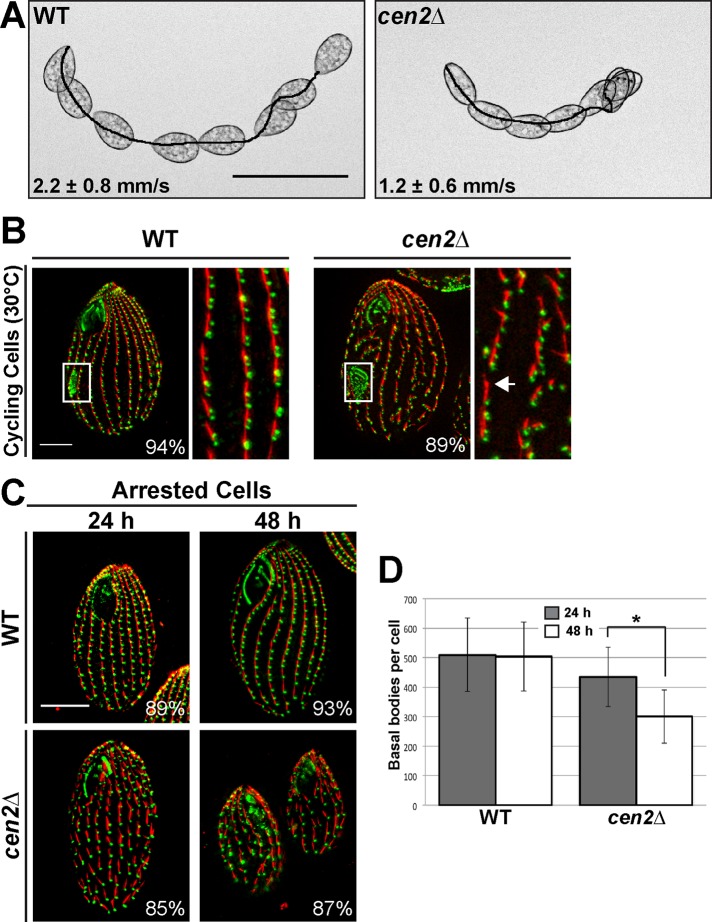
FIGURE 2:
Deletion of CEN2 leads to swimming defects and basal body maintenance defects. (A) Images showing the swimming speed of wild-type and cen2Δ cells. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Immunofluorescence images showing gaps (arrow) in the cen2Δ. White box, oral primordium, which is indicative of new basal body assembly. (C) Cells arrested by starvation and fixed 24 and 48 h after cell arrest. (B and C) Green, Cen1; red, KD fibers. Scale bar: 10 μm. Width of insets: 10 μm. Percentages indicate the frequency of observed phenotype for 100 cells. (D) Plot showing the number of basal bodies per cell at the two different time points. *, p < 0.01; n = 25 cells.