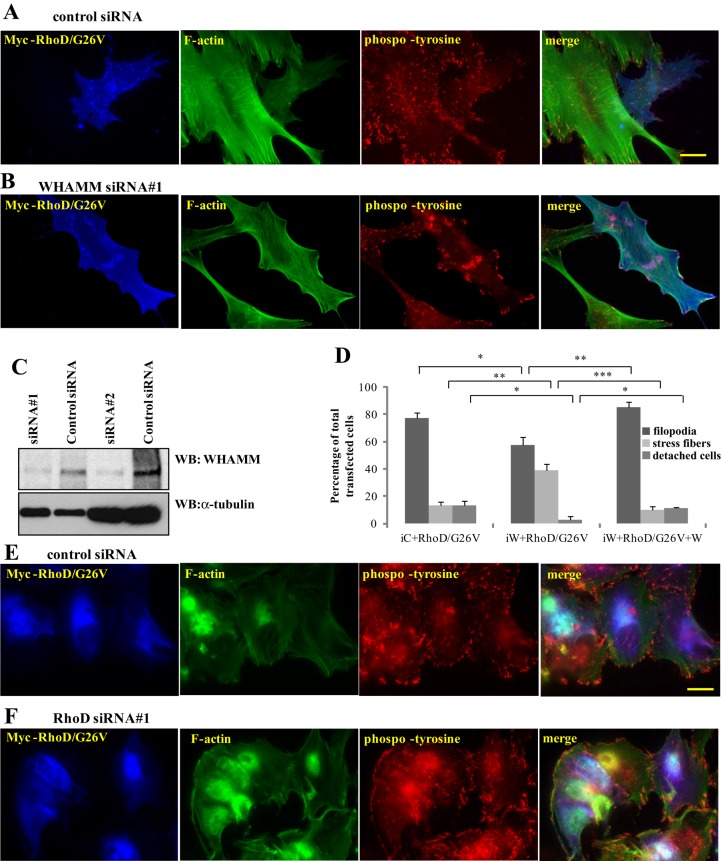
FIGURE 6:
WHAMM is required for RhoD-dependent actin reorganization. (A and B) Constitutively active RhoD/G26V has a more profound influence on the organization of the actin filament system in BJ/SV40T cells treated with a control siRNA than in cells treated with a WHAMM-specific siRNA. Myc-RhoD/G26V was visualized using rabbit anti-Myc antibodies followed by AMCA-conjugated anti-rabbit antibodies. Filamentous actin was visualized using Alexa Fluor 488–conjugated phalloidin. Focal adhesions were visualized using mouse anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies followed by TRITC anti-mouse antibodies. Scale bar: 20 μm. (C) The efficiency of a WHAMM-specific siRNA was revealed by transfecting a control siRNA or the WHAMM-specific siRNAs into human fibroblasts. WHAMM was detected using a rabbit anti-WHAMM antibody. The two siRNAs were analyzed in separate experiments, which explains why the cell number differs as demonstrated by the loading control for the two sets of experiments. (D) Quantification of the constitutively active RhoD/G26V-induced effects on the organization of the actin filament system (filopodia, stress fibers, and detached cells). iC, control siRNA; iW, WHAMM siRNA#1; W, FLAG-tagged WHAMM used to rescue the phenotype induced by knockdown of WHAMM. At least 100 transfected cells from three independent experiments were scored for cortical actin bundles and lamellipodia. The error bars represent SD. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. (E and F) FLAG-WHAMM was visualized using rabbit anti-FLAG antibodies followed by AMCA-conjugated anti-rabbit antibodies. Filamentous actin was visualized using Alexa Fluor 488–conjugated phalloidin. Focal adhesions were visualized using mouse anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies followed by TRITC-labeled anti-mouse antibodies. Scale bar: 20 μm.