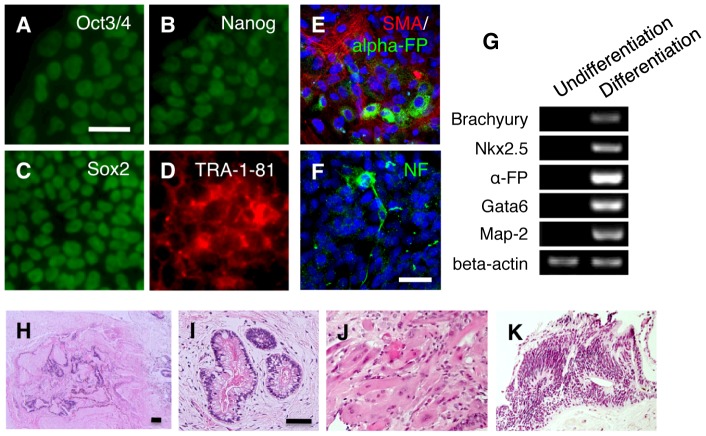
Figure 1. Characterization of iPS cell colony G.
(A–D) Immunocytochemistry for (A) Oct3/4, (B) Nanog, (C) Sox2, (D) TRA-1-81 in iPS cell colony G. Scale bar = 100 µm. (E, F) EBs generated from colony G were plated on gelatin coated dishes containing DMEM/F12 medium supplemented with 20% knockout serum replacement. After 10 days, cell differentiation was confirmed by immunocytochemistry for mesodermal (smooth muscle actin; SMA) (E), endodermal (alpha-fetoprotein; alpha-FP) (E) and ectodermal markers (neurofilament; NF) (F). Scale bar = 100 µm. (G) RT-PCR of differentiation markers in undifferentiated iPS cell colony G (Undifferentiation) and embryoid bodies derived from iPS cell colony G. Differentiation). (H–K) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of teratoma formed by transplantation of iPS cell colony G into immunodeficient mice testis. (H), Low magnification of the formed teratoma (12 weeks after injection). Endodermal (I), mesodermal (J) and ectodermal (K) tissue were observed in the teratoma.