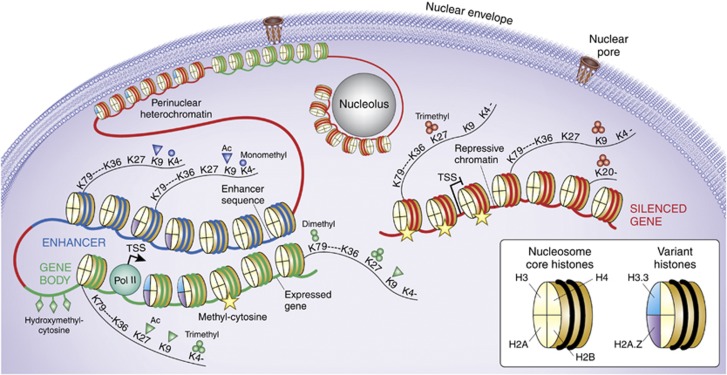
Figure 1.
The Epigenome, from nucleus to nucleosome. Schematic illustration of (green) gene poised for transcription by polymerase II (Pol II) initiation complex, with nucleosome free interval at transcription start site (TSS). (Blue) distal enhancer sequence which in loop-like structure moves in close proximity to active gene. (Red) marks a small subset of heterochromatic portions of the genome, including silenced gene and heterochromatic structures bordering the nuclear envelope and pore complex, and also the nucleolar periphery. A small subset of representative histone variants and histone H3 site-specific lysine (K) residues at N-terminal tail (K4, K9, K27, and K36) or core fold domain of the (histone) octamer (K79) and the H4K20 residue are shown as indicated, together with panel of mono- and trimethyl, or acetyl modifications that differentiate between active promoters, transcribed gene bodies, and repressive chromatin, as indicated. DNA cytosines that are hydroxymethylated at the C5 position are mostly found at active promoters, whereas methylated cytosines are positioned within body of actively transcribed genes and around repressed promoters and in constitutive heterochromatin.